Elasticsearch - OpenTelemetry Collector

The Elasticsearch app is a unified logs and metrics app that helps you monitor the availability, performance, health, and resource utilization of your Elasticsearch clusters. Preconfigured dashboards provide insight into cluster health, resource utilization, sharding, garbage collection, and search, index, and cache performance.
We use the OpenTelemetry collector to collect Elasticsearch metrics and logs.
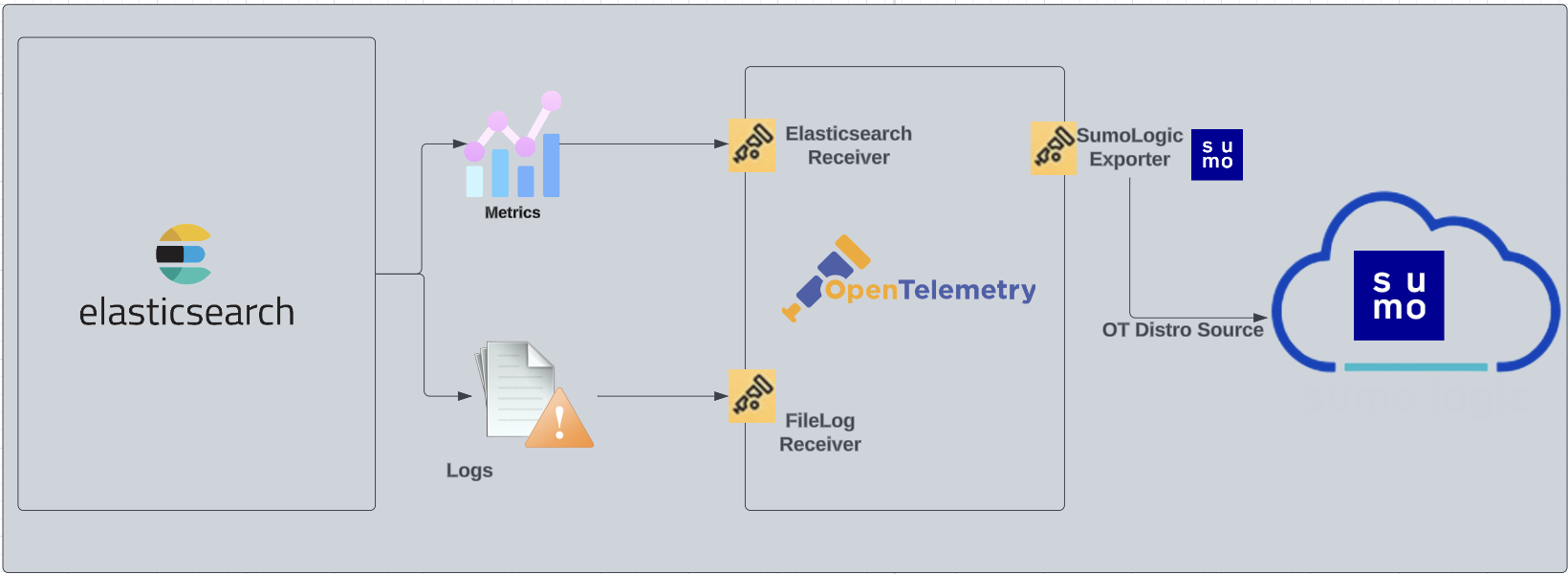
The diagram below illustrates the components of the Elasticsearch collection for each database server. OpenTelemetry collector runs on the same host as Elasticsearch, and uses the Elasticsearch Receiver to obtain Elasticsearch metrics, and the Sumo Logic OpenTelemetry Exporter to send the metrics to Sumo Logic. Elasticsearch logs are sent to Sumo Logic through a filelog receiver.
This app includes built-in monitors. For details on creating custom monitors, refer to Create monitors for Elasticsearch app.
Fields Create in Sumo Logic for Elasticsearch
Following are the Fields which will be created as part of Elasticsearch app installation, if not already present:
db.cluster.name. User configured. Enter a name to identify this Elasticsearch cluster. This cluster name will be shown in the Sumo Logic dashboards.db.system. Has a fixed value of elasticsearch.sumo.datasource. Has a fixed value of elasticsearch.db.node.name. Has the value of host name of the machine which is being monitored.
Prerequisites
For metrics collection
This receiver supports Elasticsearch versions 7.9+.
If Elasticsearch security features are enabled, you must have either the monitor or manage cluster privilege. See the Elasticsearch docs for more information on authorization and Security privileges.
For logs collection
Elasticsearch supports logging via local text log files. Elasticsearch logs have four levels of verbosity. To select a level, set loglevel to one of:
- debug. A lot of information, useful for development/testing.
- verbose. Includes information not often needed, but logs less than debug.
- notice (default value). Moderately verbose, ideal for production environments.
- warning. Only important/critical messages are logged.
All logging settings are located in Elasticsearch.conf. By default, Elasticsearch logs are stored in /var/log/elasticsearch/ELK-<Clustername>.log. The default directory for log files is listed in the Elasticsearch.conf file.
For Linux systems with ACL Support, the otelcol install process should have created the ACL grants necessary for the otelcol system user to access default log locations. You can verify the active ACL grants using the getfacl command. Install the ACL in your Linux environment, if not installed.
The required ACL may not be supported for some rare cases, for example, Linux OS Distro, which is officially not supported by Sumo Logic. In this case, you can run the following command to explicitly grant the permissions.
sudo setfacl -R -m d:u:otelcol-sumo:r-x,d:g:otelcol-sumo:r-x,u:otelcol-sumo:r-x,g:otelcol-sumo:r-x <PATH_TO_LOG_FILE>
Run the above command for all the log files in the directory that need to be ingested, which are not residing in the default location.
If Linux ACL Support is not available, traditional Unix-styled user and group permission must be modified. It should be sufficient to add the otelcol system user to the specific group that has access to the log files.
For Windows systems, log files which are collected should be accessible by the SYSTEM group. Use the following set of PowerShell commands if the SYSTEM group does not have access.
$NewAcl = Get-Acl -Path "<PATH_TO_LOG_FILE>"
# Set properties
$identity = "NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM"
$fileSystemRights = "ReadAndExecute"
$type = "Allow"
# Create new rule
$fileSystemAccessRuleArgumentList = $identity, $fileSystemRights, $type
$fileSystemAccessRule = New-Object -TypeName System.Security.AccessControl.FileSystemAccessRule -ArgumentList $fileSystemAccessRuleArgumentList
# Apply new rule
$NewAcl.SetAccessRule($fileSystemAccessRule)
Set-Acl -Path "<PATH_TO_LOG_FILE>" -AclObject $NewAcl
Collection configuration and app installation
Follow these steps to set up and deploy the source template to collect data in Sumo Logic from a remotely managed OpenTelemetry collector.
Step 1: Set up remotely managed OpenTelemetry collector
If you want to configure your source locally, you can do so by downloading the YAML file. For details, see Configure OpenTelemetry collectors locally.
In this step, we'll install remotely managed OpenTelemetry collector and add a uniquely identifiable tag to these collectors.
- Classic UI. In the main Sumo Logic menu, Select App Catalog.
New UI. In the Sumo Logic main menu select App Catalog. - In the 🔎 Search Apps field, run a search for your desired OpenTelemetry app, then select it. For example, Apache - OpenTelemetry.
- Click the Manage dropdown and then select Add Collection.
- On the Set Up Collector page, select Add a New Collector and then click Next.
If you want to use an existing OpenTelemetry Collector, you can skip this step by selecting the Use an existing Collector option.
- Select the platform where you want to install the Sumo Logic OpenTelemetry Collector. For example, Linux.
This will generate a command that you can execute in the machine environment you need to monitor. Once executed, it will install the Sumo Logic OpenTelemetry Collector.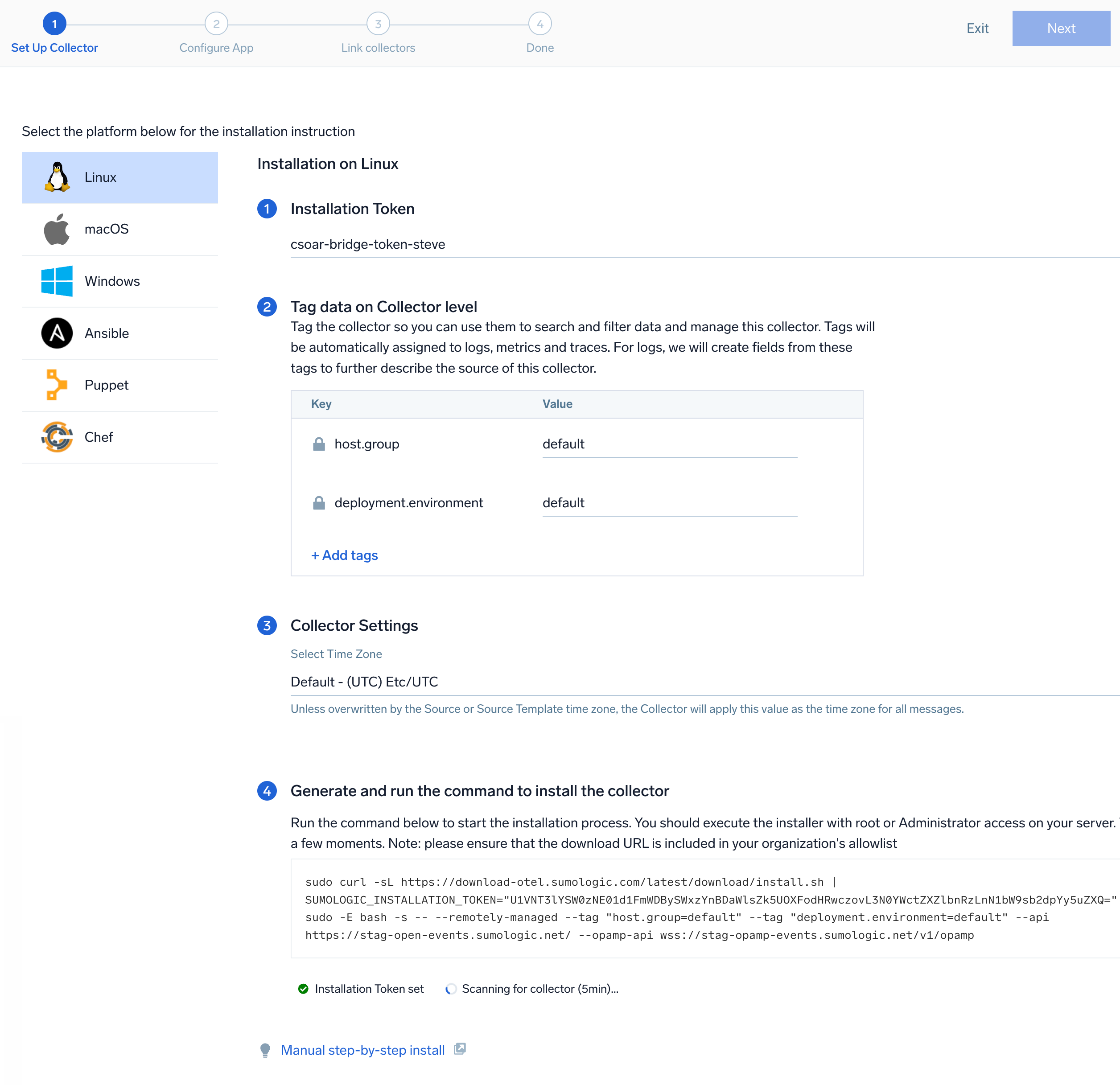 The installation commands now include a
The installation commands now include a --remotely-managedflag. When this flag is used, a remotely managed collector is installed automatically instead of a locally managed one. If you prefer to use a locally managed collector, simply remove the flag from the installation command.
Step 2: Configure the source template
In this step, you will configure the YAML required for Elasticsearch collection. Below are the inputs required for configuration:
- Name. Name of the source template.
- Description. Description for the source template.
- Log Filepath. Location where the Elasticsearch logs are logged. Please refer to your elasticsearch.conf file.
- Endpoint. Enter the url of the server you need to monitor. (default:
localhost:9200). - Username. Enter the Elasticsearch username.
- Password Environment Variable Name. Enter the Elasticsearch password environment variable name.
- Fields/Metadata. You can provide any customer fields to be tagged with the data collected. By default, Sumo Logic tags
_sourceCategorywith the value otel/elasticsearch user needs to provide the value fordb.cluster.name.
Timestamp Parsing. You can configure timestamp parsing for logs ingested using this source template. For more information, see Timestamps, Time Zones, Time Ranges, and Date Formats for the OpenTelemetry Collector.
Processing Rules. You can add processing rules for logs/metrics collected. To learn more, refer to Processing Rules.
Step 3: Push the source template to the desired remotely managed collectors
A new source template will always be created with the latest version of the source template.
Follow the below steps to create a data collection configuration to gather the required logs and link them to all the collectors with the help of collector tags.
- Complete the source template form with the name and file path for your logs (for example, error logs or access logs), then click Next.
- Under Link Collectors, you will have the option to link the collectors using the collector name or by adding tags to find the group of collectors (for example,
application = Apache).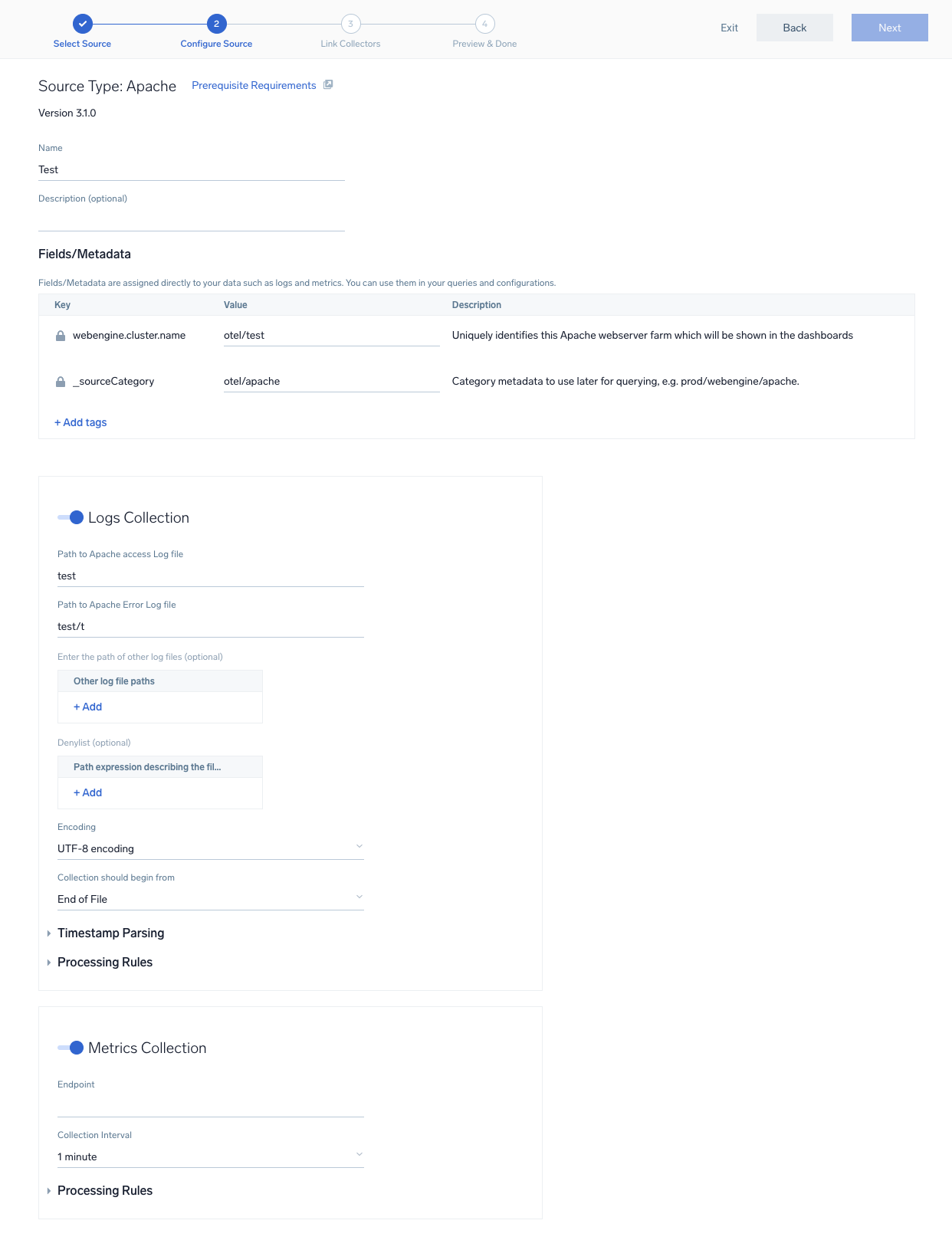
- Preview and confirm the collectors that will be linked (fetched automatically) to the newly created source template.
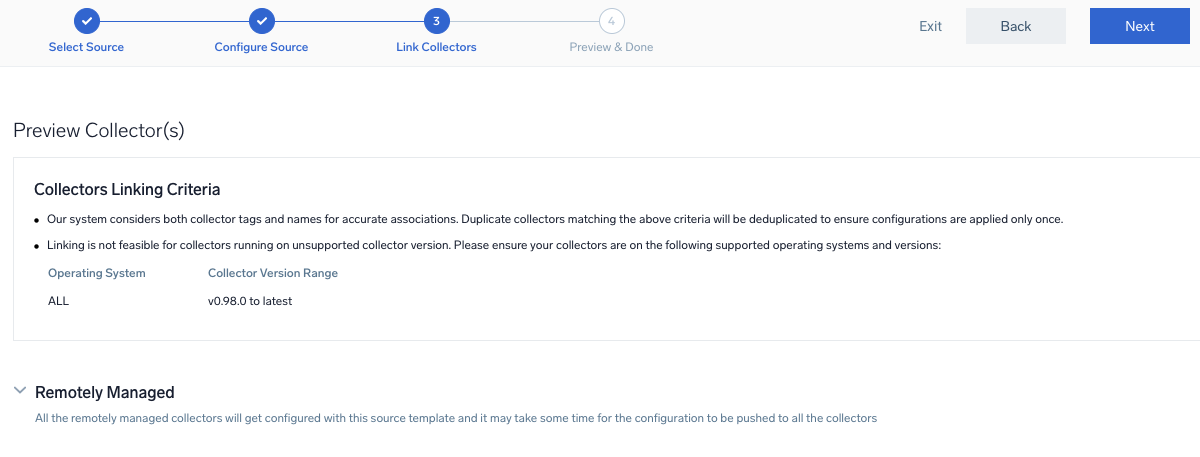
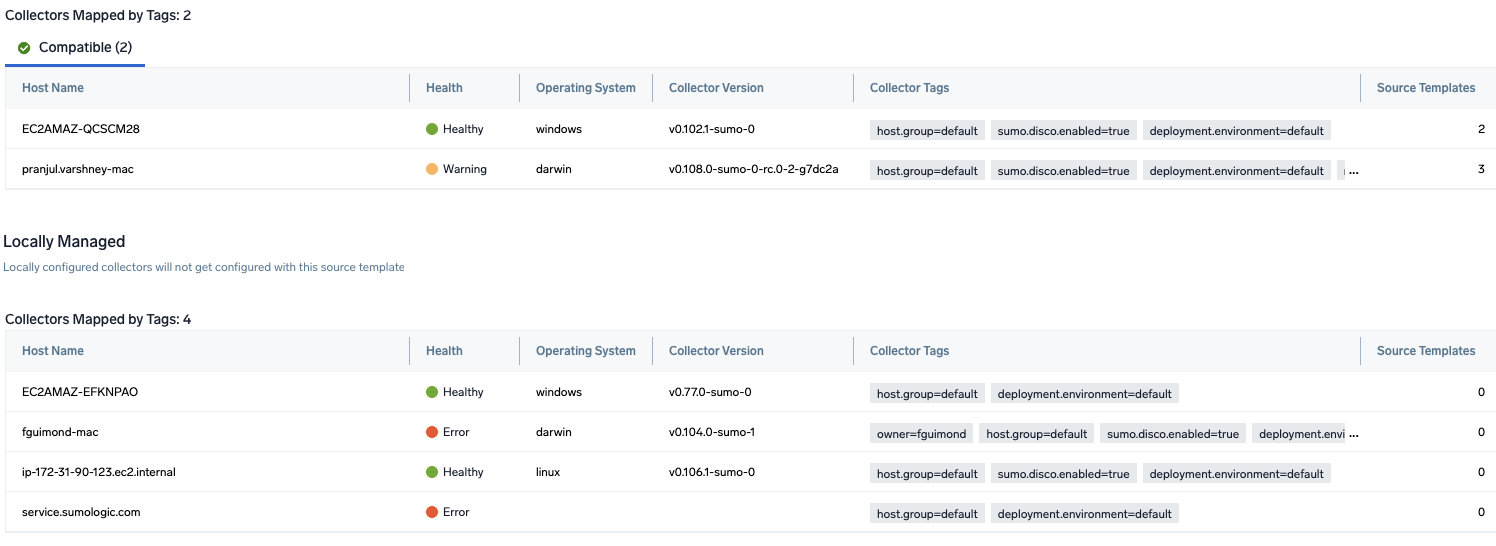
- Click Next to complete the source template creation. In the background, the system will apply the configuration to all the linked collectors and will start collecting the respective telemetry data from the remote host (in the example, it would start collecting Apache error logs).
- Click the Log Search or Metrics Search icons to search for and analyze your data collected for this source template.
Sample log messages
{
"type":"server",
"timestamp":"2021-07-12T11:42:25,862+07:00",
"level":"INFO",
"component":"o.e.x.s.a.s.FileRolesStore",
"cluster.name":"elasticsearch",
"node.name":"v103-157-218-134.3stech.vn",
"message":"parsed [0] roles from file [/etc/elasticsearch/roles.yml]"
}
Sample metrics
{
"queryId":"A",
"_source":"sumo_hosted_collector_otel_elasticsearch",
"state":"completed",
"thread_pool_name":"analyze",
"elasticsearch.node.name":"ip-172-31-86-95",
"elasticsearch.cluster.name":"elasticsearch",
"metric":"elasticsearch.node.thread_pool.tasks.finished",
"db.cluster.name":"elastic_otel_cluster",
"_collectorId":"000000000C5B7100",
"deployment.environment":"otel_elastic_dev",
"_sourceId":"0000000000000000",
"unit":"{tasks}",
"db.system":"elasticsearch",
"_sourceHost":"sumoOtelelasticsearch",
"_collector":"sumo_hosted_collector_otel_elasticsearch",
"max":0,
"min":0,
"avg":0,
"sum":0,
"latest":0,
"count":2
}
Sample queries
Sample logs query
This is a sample log query from the Errors panel.
db.system=elasticsearch %"deployment.environment"={{deployment.environment}} db.cluster.name={{db.cluster.name}} ERROR | json "log" as _rawlog nodrop
| if (isEmpty(_rawlog), _raw, _rawlog) as _raw
| json field=_raw "timestamp" as timestamp
| json field=_raw "level" as level
| json field=_raw "component" as es_component
| json field=_raw "message" as message
| where level = "ERROR"
| count
Sample metrics query
This is a sample metrics query from the JVM Memory Used (MB) panel.
deployment.environment=* metric=jvm.memory.heap.used db.cluster.name=* db.node.name=* | sum by db.cluster.name, db.node.name
Viewing Elasticsearch dashboards
All dashboards have a set of filters that you can apply to the entire dashboard. Use these filters to drill down and examine the data to a granular level.
- You can change the time range for a dashboard or panel by selecting a predefined interval from a drop-down list, choosing a recently used time range, or specifying custom dates and times. Learn more.
- You can use template variables to drill down and examine the data on a granular level. For more information, see Filtering Dashboards with Template Variables.
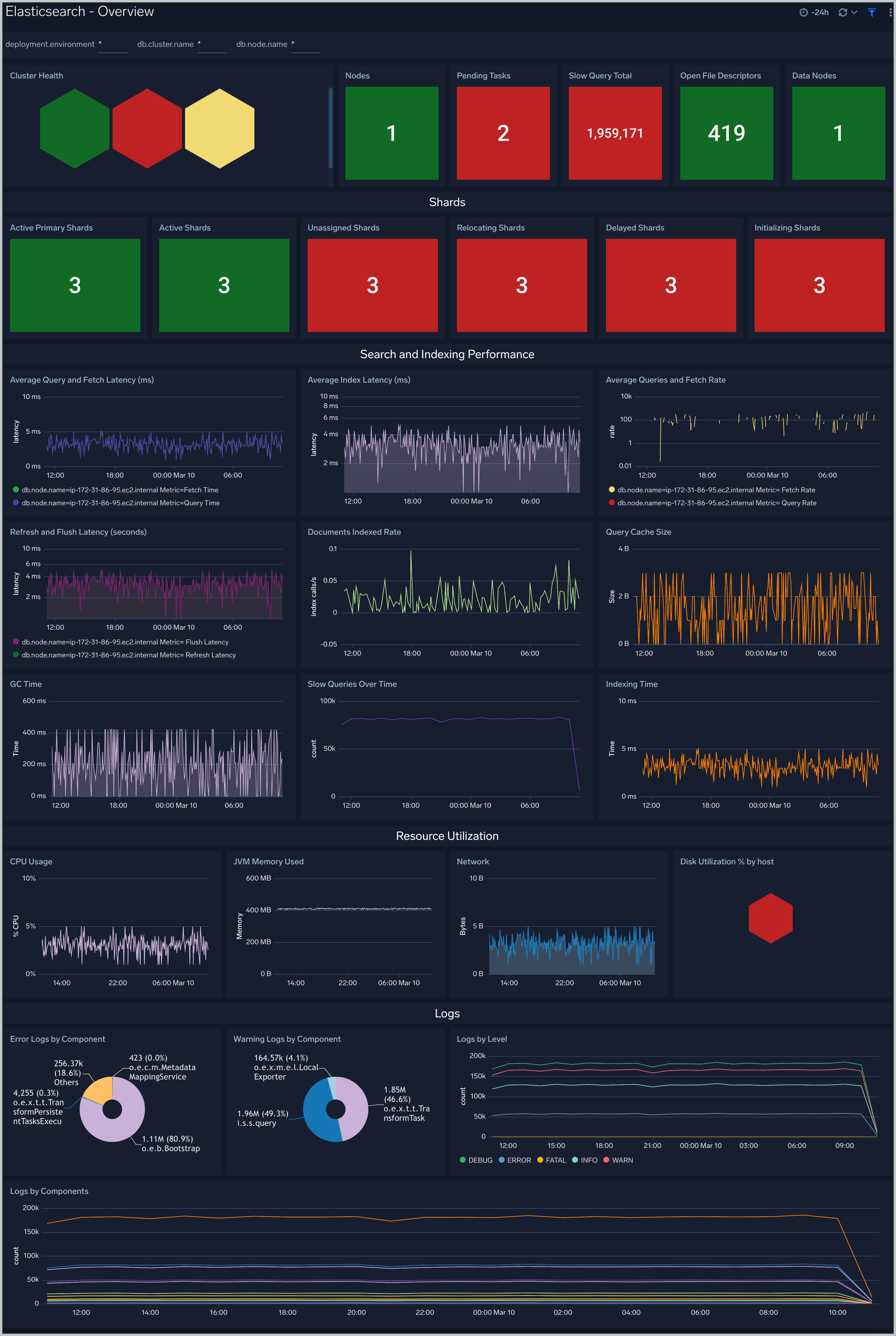
Overview
The Elasticsearch - Overview dashboard provides the health of Elasticsearch clusters, shards analysis, resource utilization of Elasticsearch host and clusters, search and indexing performance.
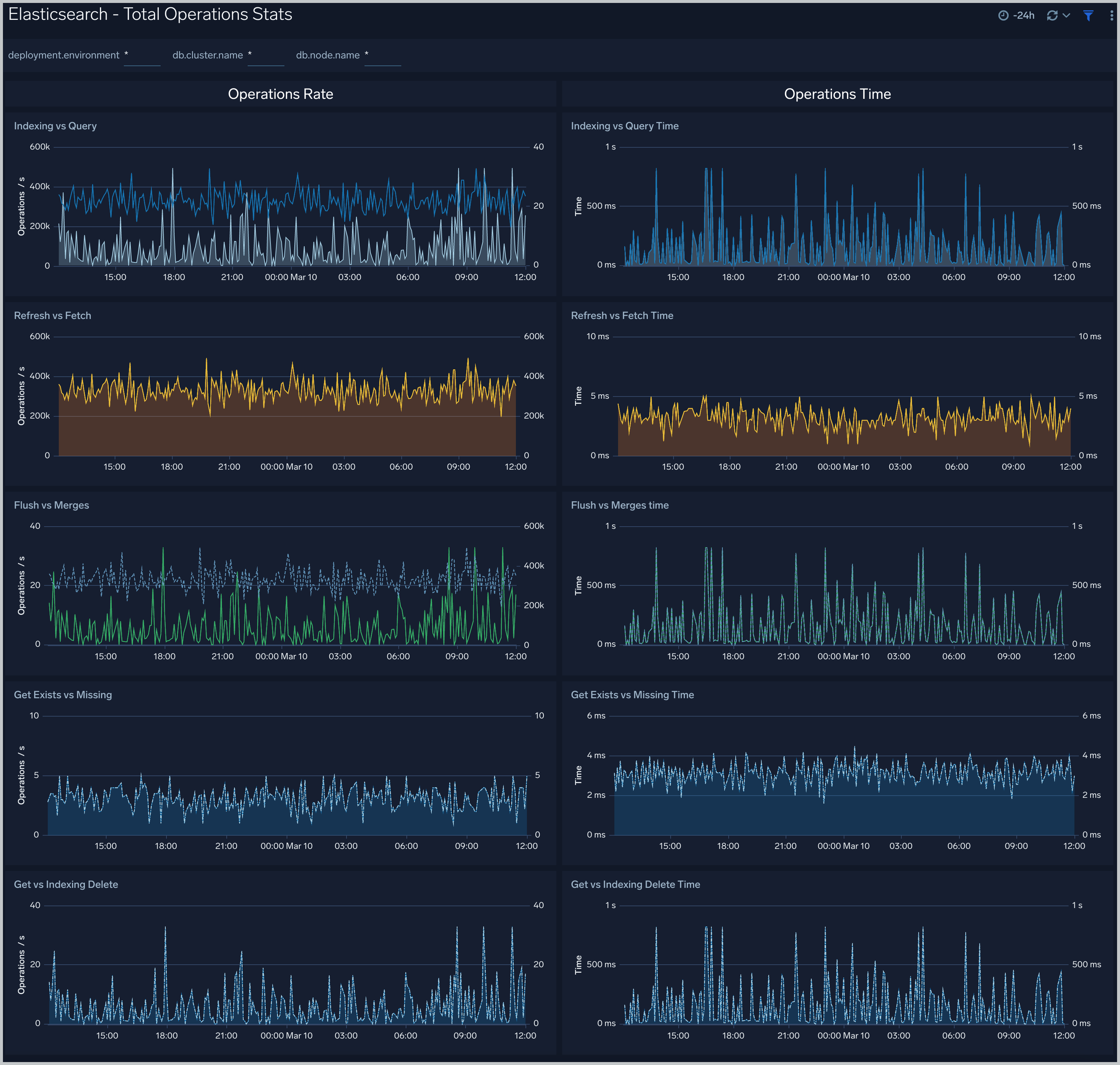
Total Operations Stats
The Elasticsearch - Total Operations stats dashboard provides information on the operations of the Elasticsearch system.
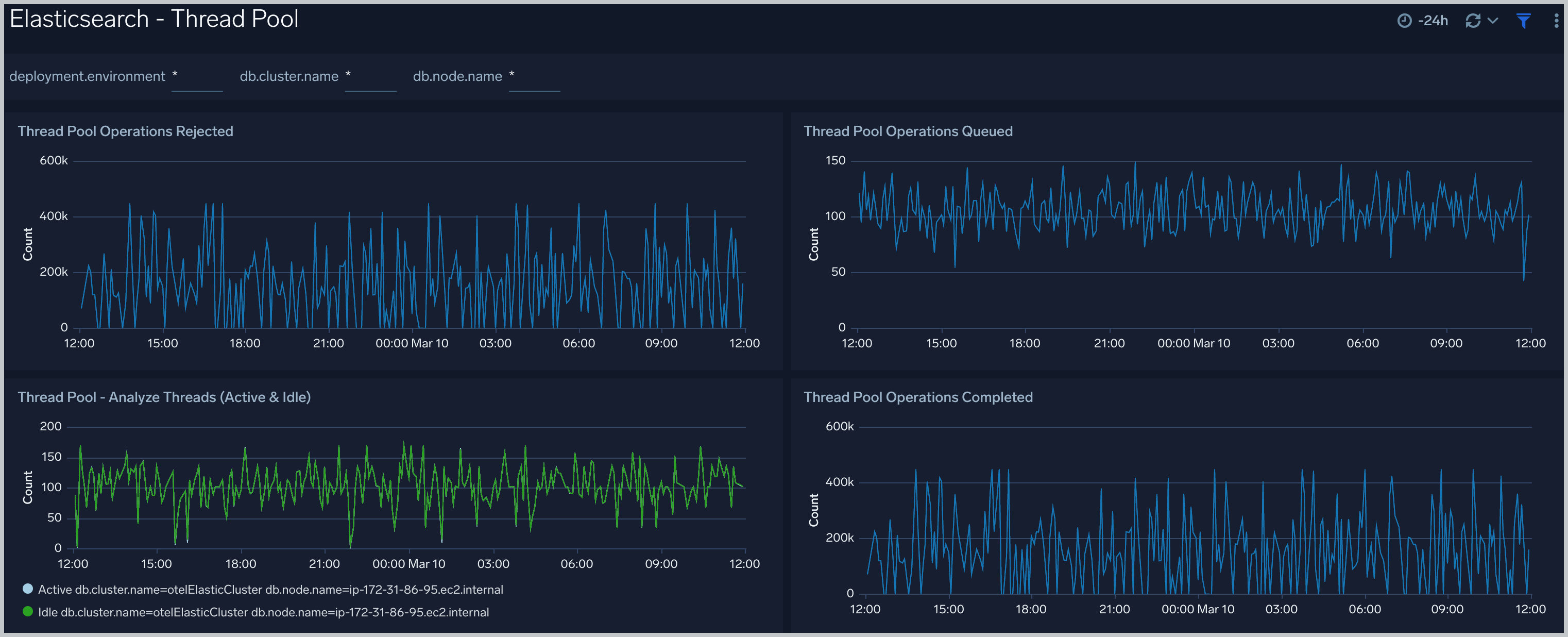
Thread Pool
The Elasticsearch - Thread Pool dashboard analyzes thread pools operations to manage memory consumption of nodes in the cluster.
Resource
The Elasticsearch - Resource dashboard monitors JVM Memory, Network, Disk, Network and CPU of Elasticsearch node.
Performance Stats
The Elasticsearch - Performance Stats dashboard performance statistics such as latency and Translog operations and size.
Indices
The Elasticsearch - Indices dashboard monitors Index operations, size and latency. It also provides analytics on doc values, fields, fixed bitsets, and terms memory.
Documents
The Elasticsearch - Documents dashboard provides analytics and monitoring on Elasticsearch documents.
Caches
The Elasticsearch - Caches dashboard allows you to monitor query cache size, evictions and field data memory size.
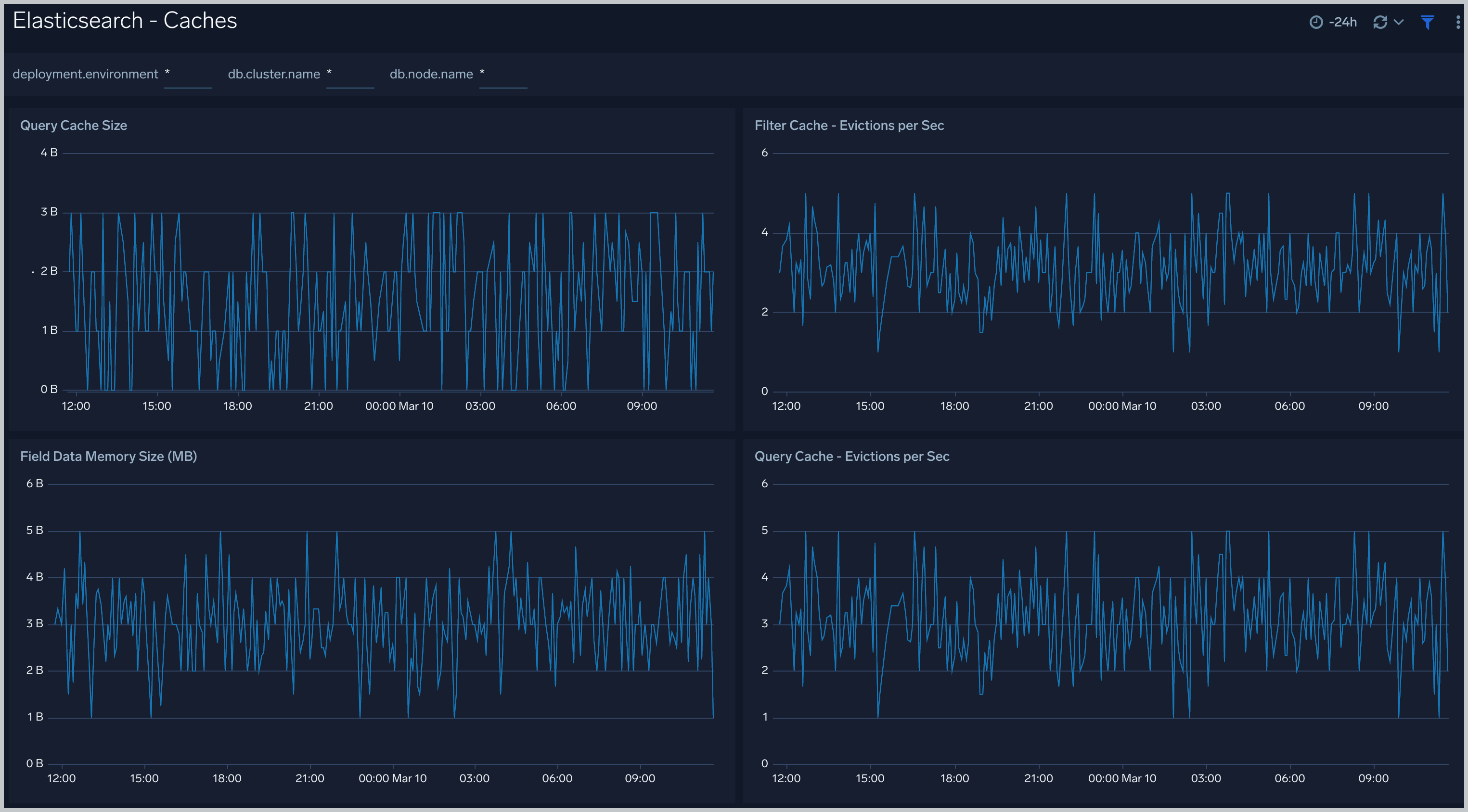
Errors And Warnings
The Elasticsearch - Errors And Warnings dashboard shows errors and warnings by Elasticsearch components.
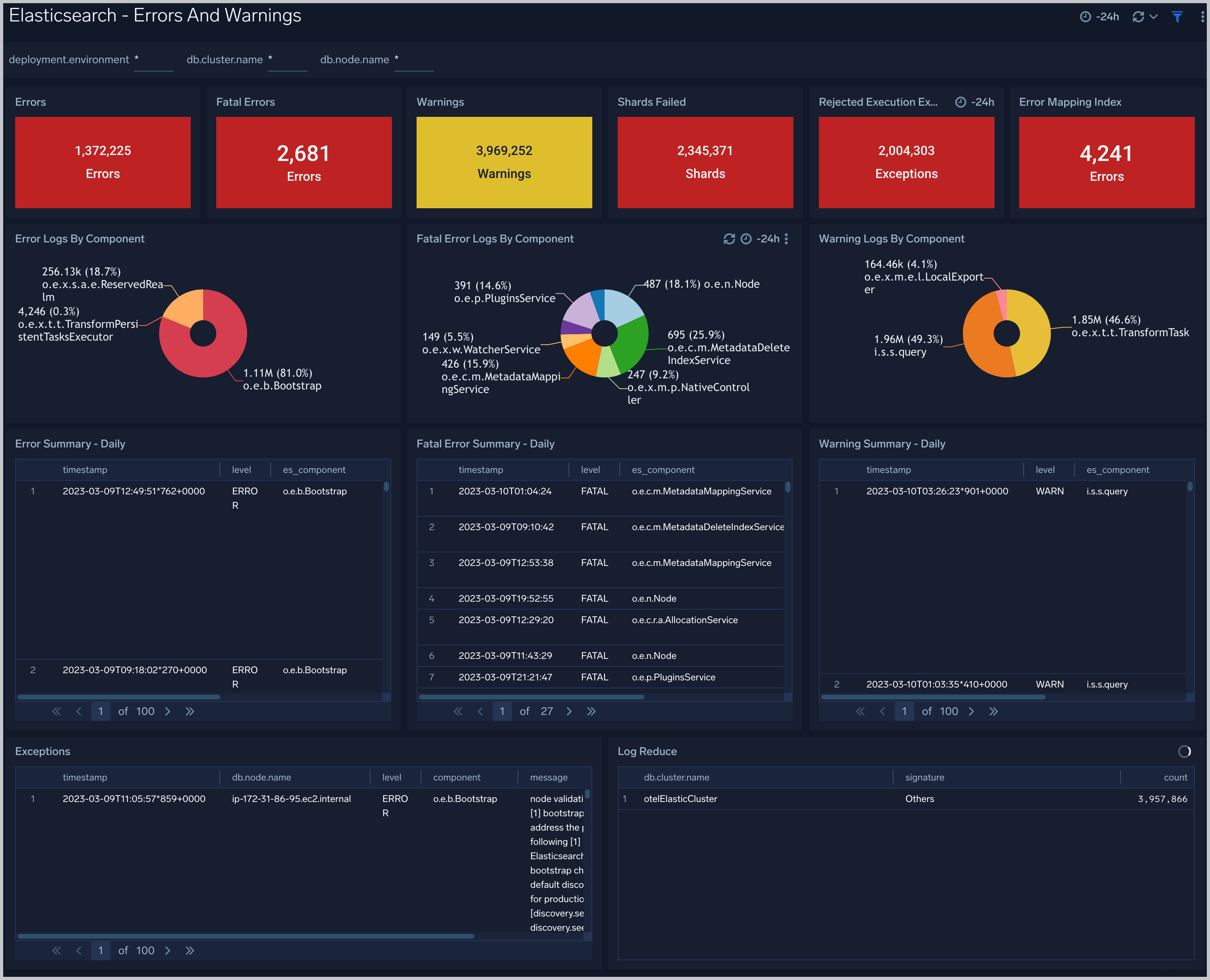
Garbage Collection
The Elasticsearch - Garbage Collector dashboard provides information on the garbage collection of the Java Virtual Machine.
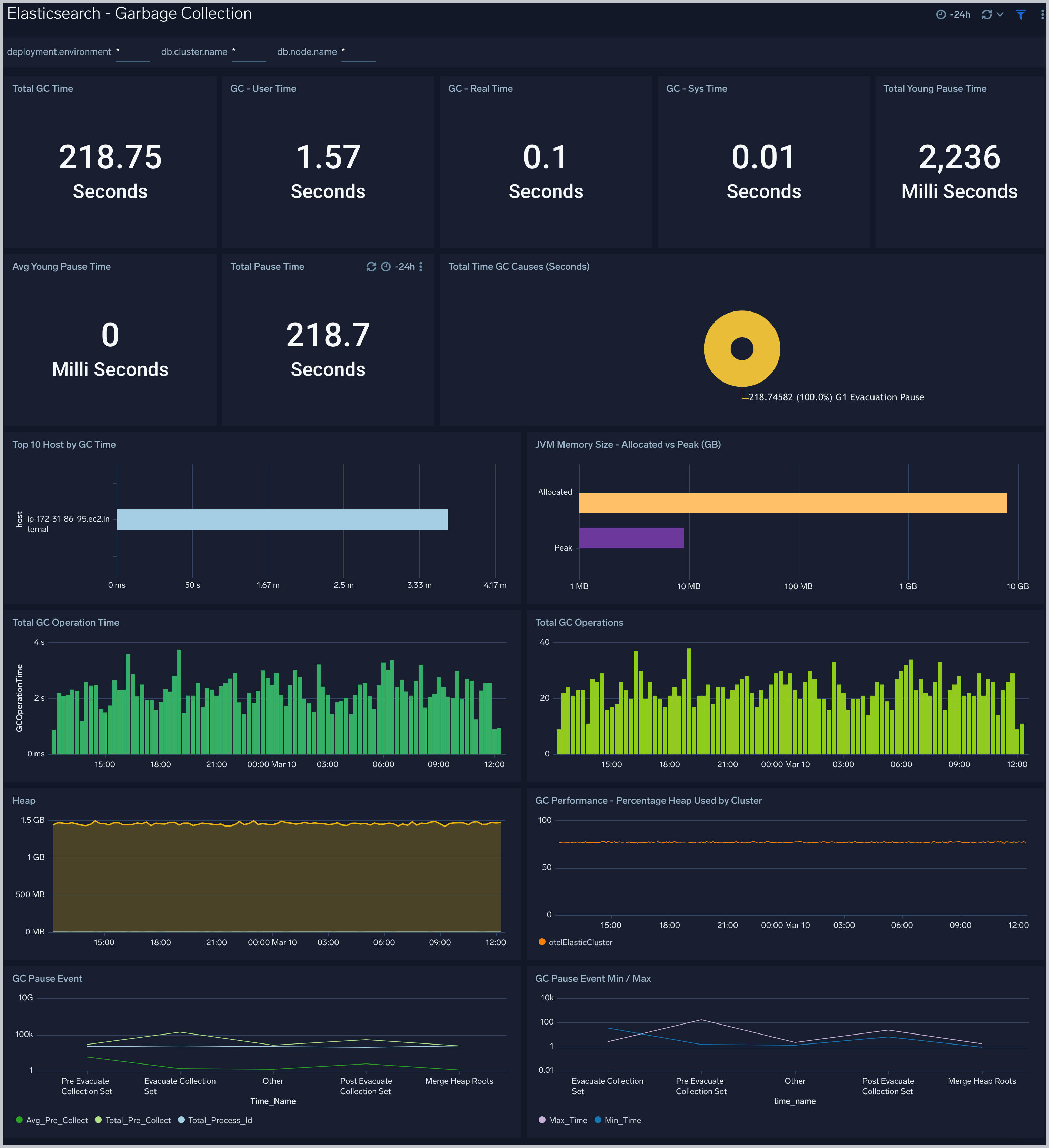
Login And Connections
The Elasticsearch - Login And Connections dashboard shows geo location of client connection requests, failed connection logins and count of failed login attempts.
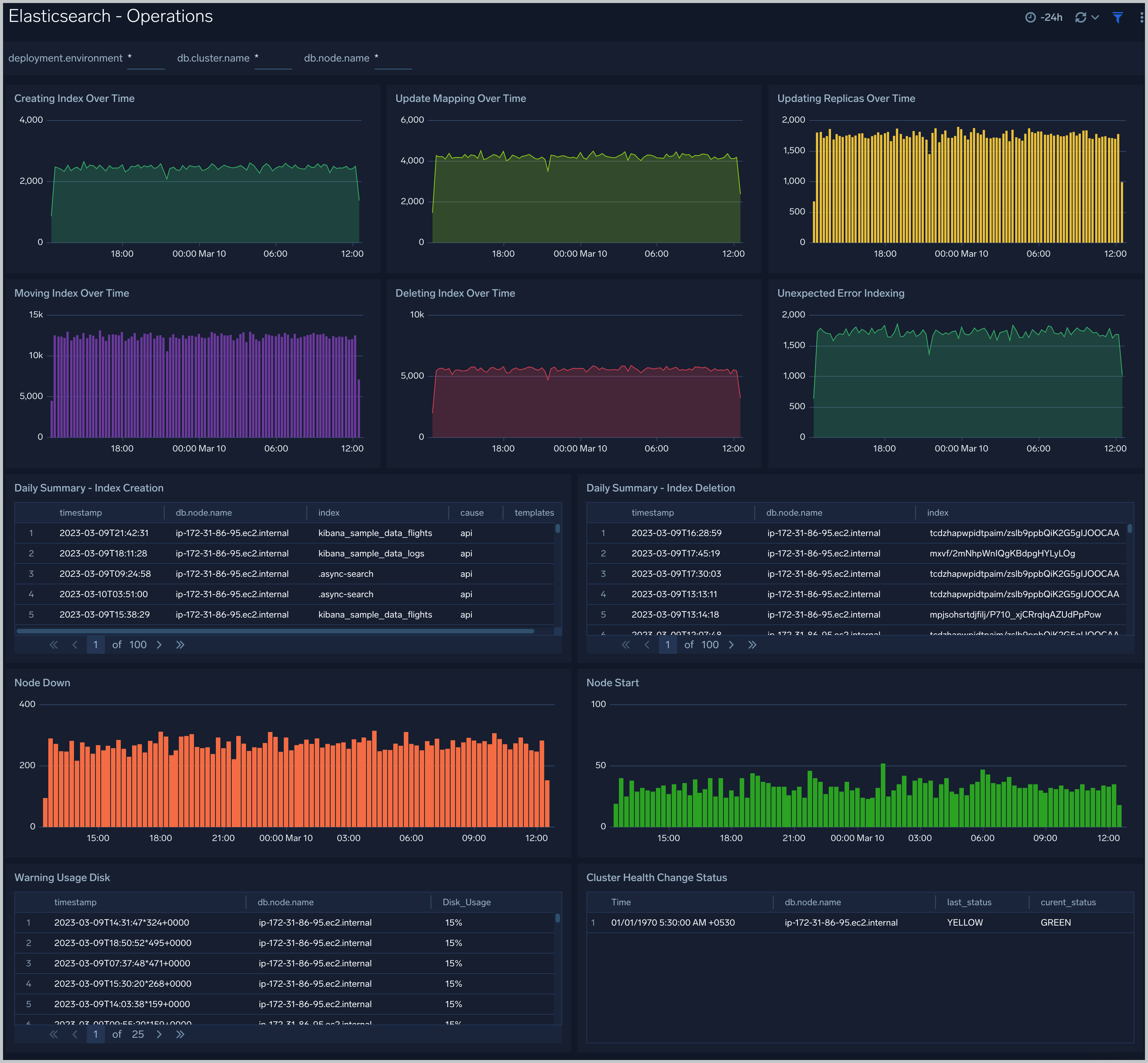
Operations
The Elasticsearch - Operations dashboard allows you to monitor server stats and events such as node up/down, index creation/deletion. It also provides disk usage and cluster health status.
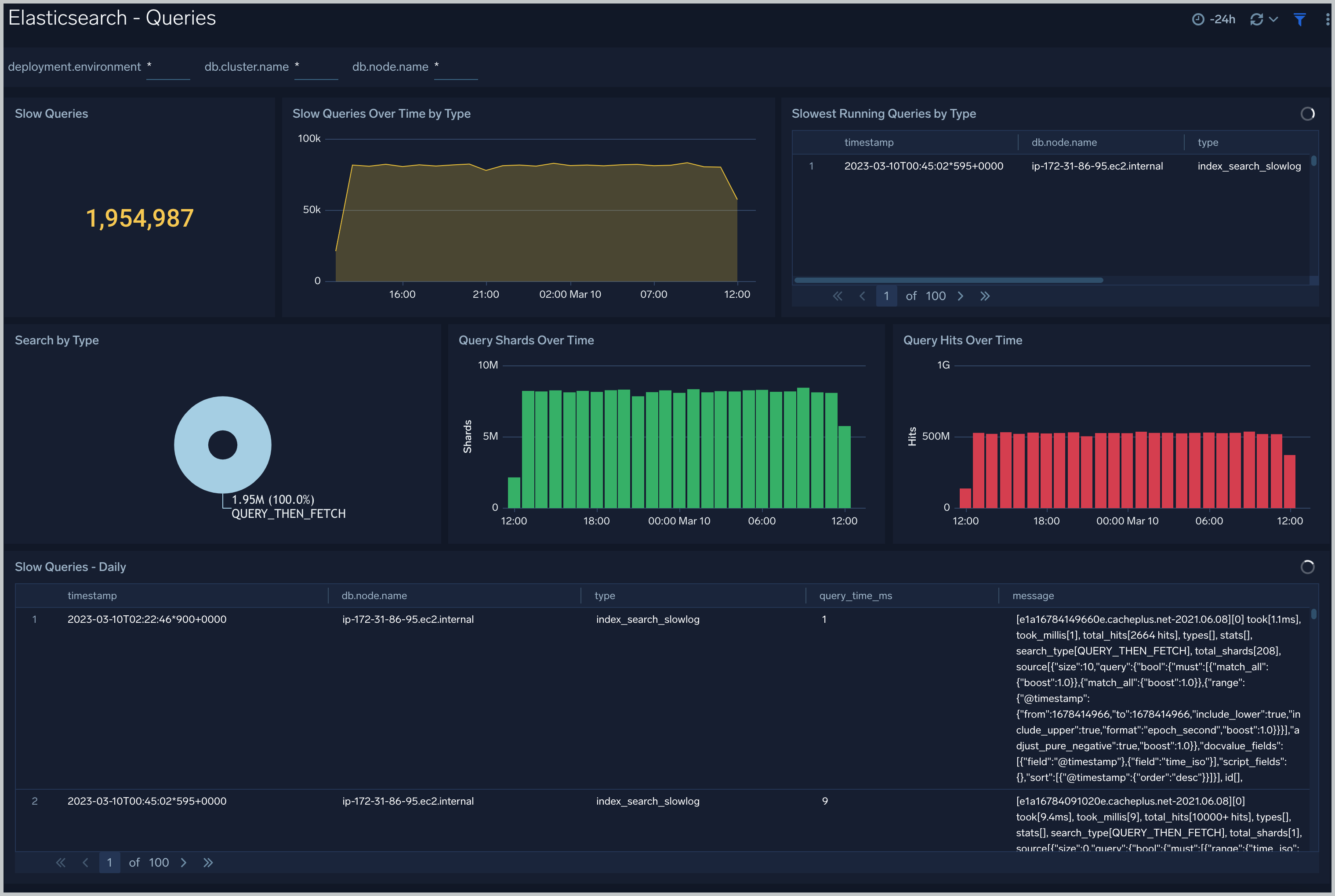
Queries
The Elasticsearch - Queries dashboard shows Elasticsearch provides analytics on slow queries, and query shards.
Create monitors for Elasticsearch app
From your App Catalog:
- From the Sumo Logic navigation, select App Catalog.
- In the Search Apps field, search for and then select your app.
- Make sure the app is installed.
- Navigate to What's Included tab and scroll down to the Monitors section.
- Click Create next to the pre-configured monitors. In the create monitors window, adjust the trigger conditions and notifications settings based on your requirements.
- Scroll down to Monitor Details.
- Under Location click on New Folder.
note
By default, monitor will be saved in the root folder. So to make the maintenance easier, create a new folder in the location of your choice.
- Enter Folder Name. Folder Description is optional.
tip
Using app version in the folder name will be helpful to determine the versioning for future updates.
- Click Create. Once the folder is created, click on Save.
Elasticsearch alerts
| Alert Name | Alert Description and conditions | Alert Condition | Recover Condition |
|---|---|---|---|
Elasticsearch - Cluster Red Alert | Elasticsearch Cluster red health status. | Count > = 1 | Count < 1 |
Elasticsearch - Cluster Yellow Alert | Elasticsearch Cluster yellow health status. | Count > 1 | Count < = 1 |
Elasticsearch - Disk Out of Space Alert | This alerts gets triggered when disk usage is over 90%. | Count > 90 | Count < = 90 |
Elasticsearch - Error Log Too Many Alert | This alert gets triggered when error logs exceeds threshold. | Count > = 1000 | Count < 1000 |
Elasticsearch - Healthy Data Nodes Alert | This alert gets triggered when missing data node in Elasticsearch cluster. | Count < = 1 | Count > 1 |
Elasticsearch - Heap Usage Too High Alert | This alert gets triggered when heap usage is over 90%. | Count > 90 | Count < = 90 |
Elasticsearch - Initializing Shards Too Long Alert | This alerts gets triggered when shard initialization takes more than 5 min. | Count > = 5 | Count < 5 |
Elasticsearch - Pending Tasks Alert | This alert gets triggered when Elasticsearch has pending tasks. | Count > = 5 | Count < 5 |
Elasticsearch - Query Time Slow Alert | This alert gets triggered when slow query time greater than 5 ms. | Count >= 1 | Count < 1 |
Elasticsearch - Query Time Too Slow Alert | This alert gets triggered when Slow Query Too High (10 ms). | Count > = 1 | Count < 1 |
Elasticsearch - Relocating Shards Too Long Alert | This alert gets triggered when shards relocation take more than 5 min. | Count > = 5 | Count < 5 |
Elasticsearch - Too Many Slow Query Alert | This alert gets triggered when too many slow queries are found in 5 minutes window. | Count > = 10 | Count < 10 |
Elasticsearch - Unassigned Shards Alert | This alert gets triggered when Elasticsearch has unassigned shards. | Count > 5 | Count < = 5 |