Redis - OpenTelemetry Collector

Redis is an in-memory data structure that implements a distributed, in-memory key-value database with durability options.
The Sumo Logic app for Redis helps you monitor the Redis database cluster. The preconfigured dashboards provide detailed analysis based on logs and metrics. The panels provide details such as RDBMemory Usage, events, RDB, AOF events, resource usage, commands running, and cache hit rate.
Redis logs are sent to Sumo Logic through OpenTelemetry filelog receiver. The OpenTelemetry collector runs on the same host as Redis and uses the Redis Receiver and the Sumo Logic OpenTelemetry Exporter to send the metrics to Sumo Logic.
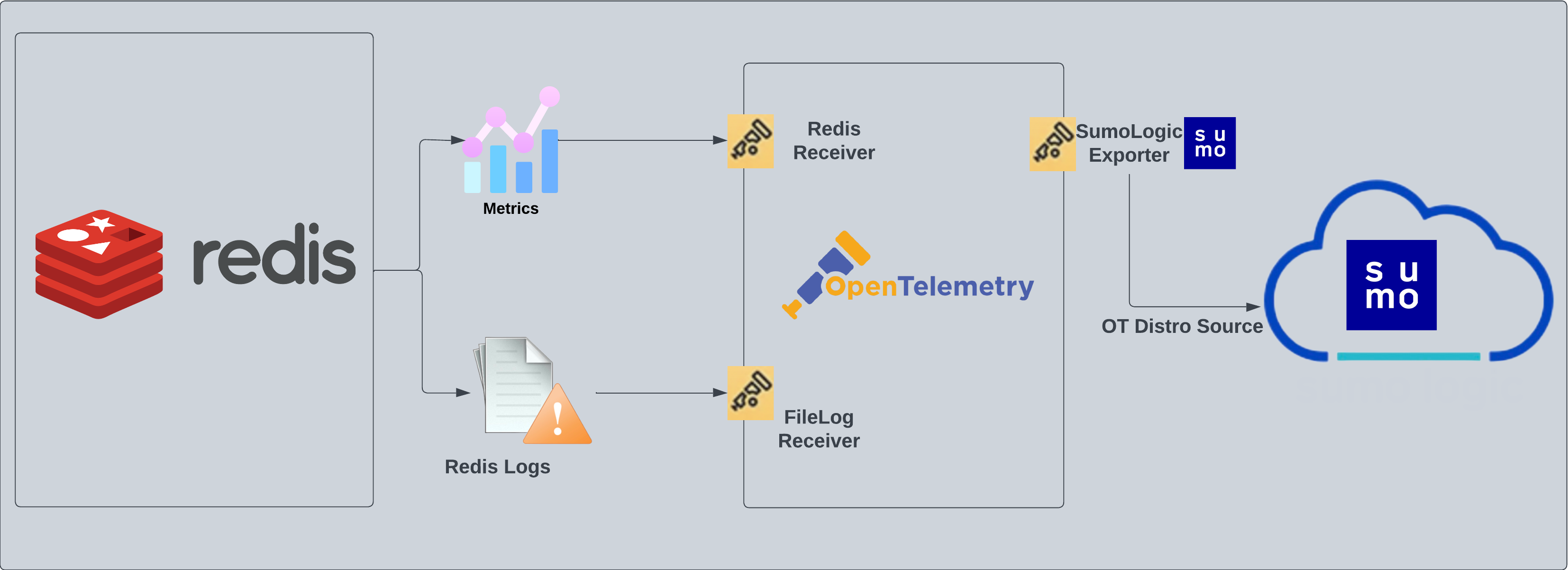
Log and metrics types
This app supports metrics and logs for Redis in Cluster mode or Standalone mode. The Redis logs are generated in files as configured in the cluster node configuration files in /etc/redis/redis.conf. For more details on Redis logs, see Redis documentation.
The app supports metrics generated by the Redis Receiver.
This app includes built-in monitors. For details on creating custom monitors, refer to the Create monitors for Redis app.
Creating fields in Sumo Logic for Redis
The following are fields that will be created as part of the Redis App install if not already present.
db.cluster.name. User configured. Enter a name to identify this Redis cluster. This cluster name will be shown in the Sumo Logic dashboards.db.system. Has fixed value of redis.deployment.environment. User configured. This is the deployment environment where the Redis cluster resides. For example: dev, prod, or qa.db.node.name. Has the value of host name of the machine which is being monitored.sumo.datasource. Has fixed value of redis.
Prerequisites
For metrics collection
The Redis INFO command returns information and statistics about a Redis server (see Redis INFO for details). The Redis receiver extracts values from the result and converts them to OpenTelemetry metrics.
For logs collection
This section provides instructions for configuring log collection for Redis running on a non-Kubernetes environment. By default, Redis logs are stored in a log file.
Follow the instructions to set up log collection:
- To configure the Redis log file, locate your local
redis.confconfiguration file in the database directory. By default, Redis logs are stored in/var/log/redis/redis-server.log. - After determining the location of conf file, open your
redis.confconfiguration file in a text editor to modify its logging parameters as such:- Specify the server verbosity level. The value
loglevelin conf file can be set to one of the following, in ascending order of severity:debug,verbose,notice,warning. - Specify the log file name. Also the empty string can be used to force Redis to log on the standard output. If you use the standard output for logging but daemonize, logs will be sent to
/dev/nulllogfile.
- Specify the server verbosity level. The value
- Save the
redis.conffile and restart the Redis server using the command:sudo service redis-server restart.
Once the logs are configured to write to a local file, follow the steps below to configure the collection in Sumo Logic.
For Linux systems with ACL Support, the otelcol install process should have created the ACL grants necessary for the otelcol system user to access default log locations. You can verify the active ACL grants using the getfacl command. Install the ACL in your Linux environment, if not installed.
The required ACL may not be supported for some rare cases, for example, Linux OS Distro, which is officially not supported by Sumo Logic. In this case, you can run the following command to explicitly grant the permissions.
sudo setfacl -R -m d:u:otelcol-sumo:r-x,d:g:otelcol-sumo:r-x,u:otelcol-sumo:r-x,g:otelcol-sumo:r-x <PATH_TO_LOG_FILE>
Run the above command for all the log files in the directory that need to be ingested, which are not residing in the default location.
If Linux ACL Support is not available, traditional Unix-styled user and group permission must be modified. It should be sufficient to add the otelcol system user to the specific group that has access to the log files.
Collection configuration and app installation
Follow these steps to set up and deploy the source template to collect data in Sumo Logic from a remotely managed OpenTelemetry collector.
Step 1: Set up remotely managed OpenTelemetry collector
If you want to configure your source locally, you can do so by downloading the YAML file. For details, see Configure OpenTelemetry collectors locally.
In this step, we'll install remotely managed OpenTelemetry collector and add a uniquely identifiable tag to these collectors.
- Classic UI. In the main Sumo Logic menu, Select App Catalog.
New UI. In the Sumo Logic main menu select App Catalog. - In the 🔎 Search Apps field, run a search for your desired OpenTelemetry app, then select it. For example, Apache - OpenTelemetry.
- Click the Manage dropdown and then select Add Collection.
- On the Set Up Collector page, select Add a New Collector and then click Next.
If you want to use an existing OpenTelemetry Collector, you can skip this step by selecting the Use an existing Collector option.
- Select the platform where you want to install the Sumo Logic OpenTelemetry Collector. For example, Linux.
This will generate a command that you can execute in the machine environment you need to monitor. Once executed, it will install the Sumo Logic OpenTelemetry Collector.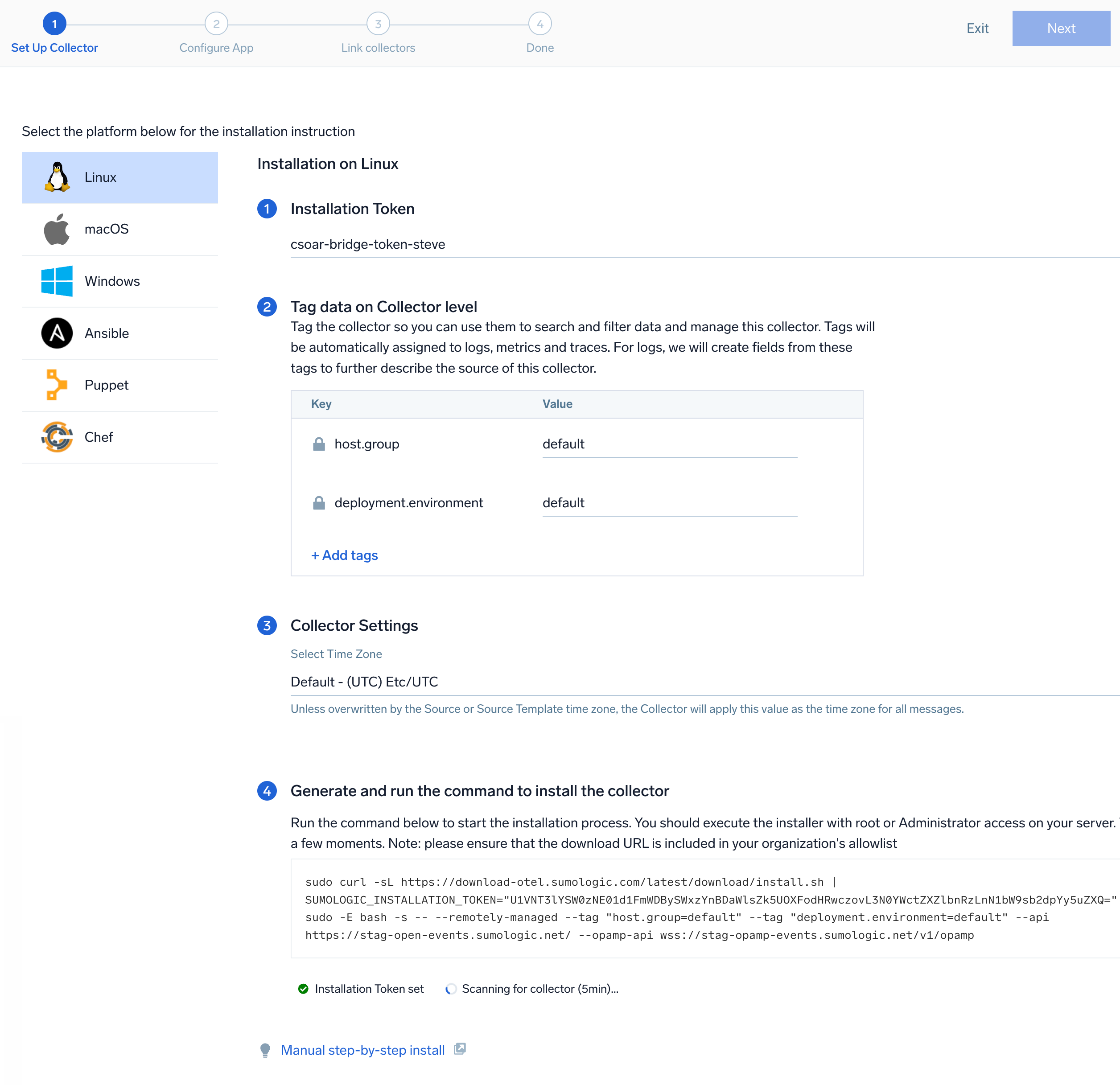 The installation commands now include a
The installation commands now include a --remotely-managedflag. When this flag is used, a remotely managed collector is installed automatically instead of a locally managed one. If you prefer to use a locally managed collector, simply remove the flag from the installation command.
Step 2: Configure the source template
- Name. Name of the source template.
- Description. Description for the source template.
- Fields/Metadata. You can provide any customer fields to be tagged with the data collected. By default, sumo tags
_sourceCategorywith the value otel/redis. - File Path. Provide the file which needs to be read by OpenTelemetry agent. You can provide path to multiple files by adding new entry to it.
- DenyList. Provide path expression describing the files to be excluded.
- Endpoint. (Default:
localhost:6379.) The hostname and port of the Redis instance, separated by a colon. - Username (Optional). Enter the Redis username in case you are using a specific user for monitoring.
- Password Environment Variable Name (Required). Enter the Redis password environment variable name.
Timestamp Parsing. You can configure timestamp parsing for logs ingested using this source template. For more information, see Timestamps, Time Zones, Time Ranges, and Date Formats for the OpenTelemetry Collector.
Processing Rules. You can add processing rules for logs/metrics collected. To learn more, refer to Processing Rules.
Step 3: Push the source template to the desired remotely managed collectors
A new source template will always be created with the latest version of the source template.
Follow the below steps to create a data collection configuration to gather the required logs and link them to all the collectors with the help of collector tags.
- Complete the source template form with the name and file path for your logs (for example, error logs or access logs), then click Next.
- Under Link Collectors, you will have the option to link the collectors using the collector name or by adding tags to find the group of collectors (for example,
application = Apache).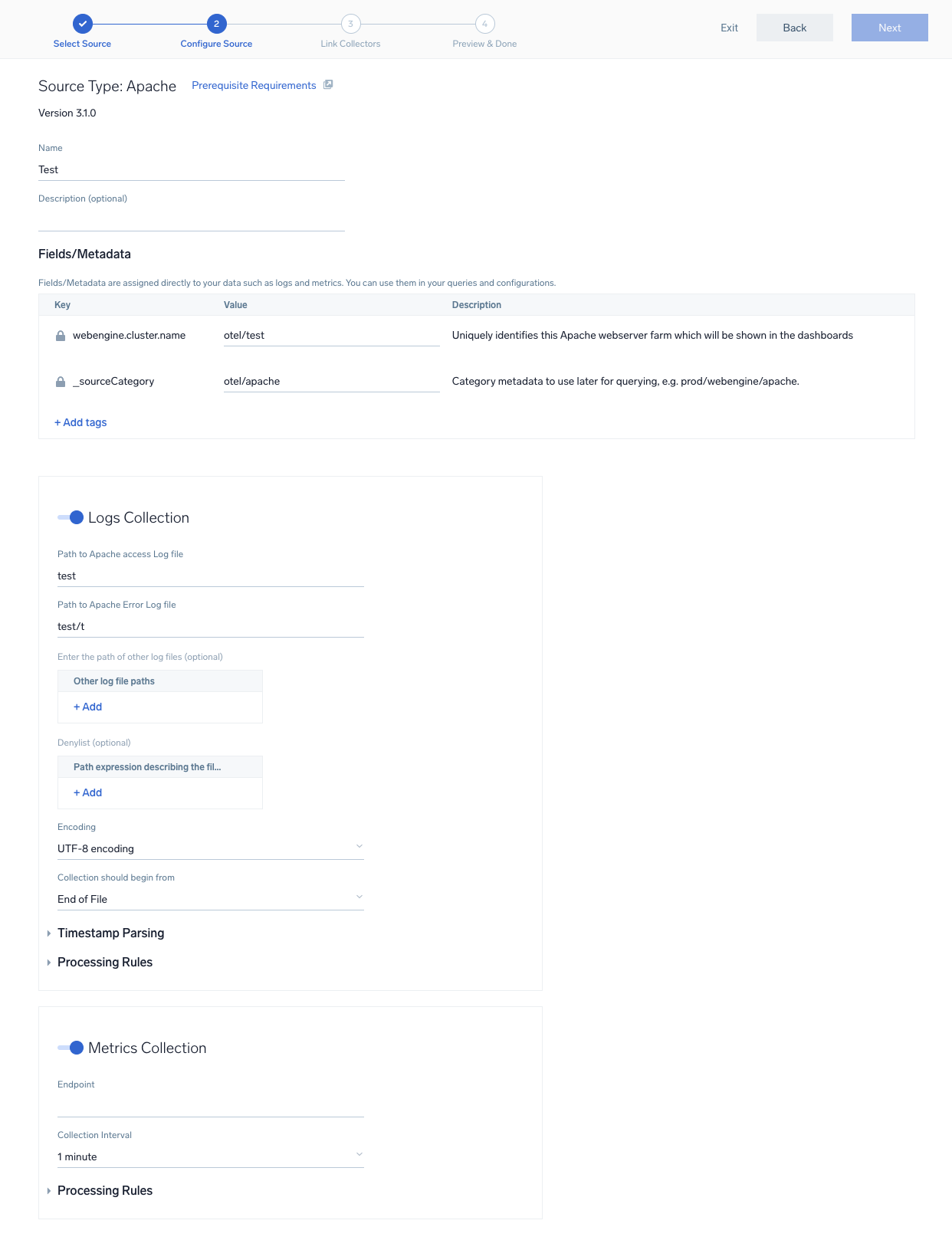
- Preview and confirm the collectors that will be linked (fetched automatically) to the newly created source template.
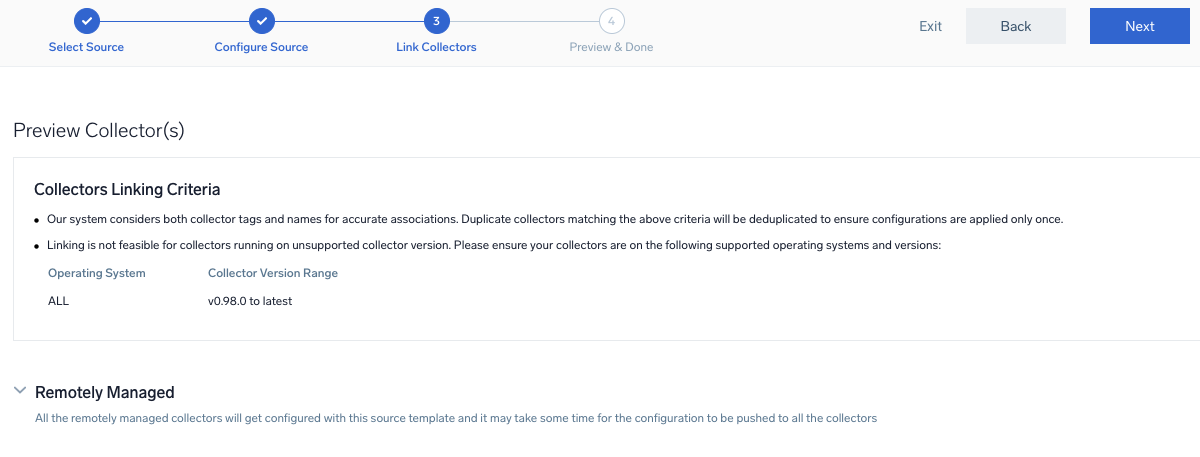
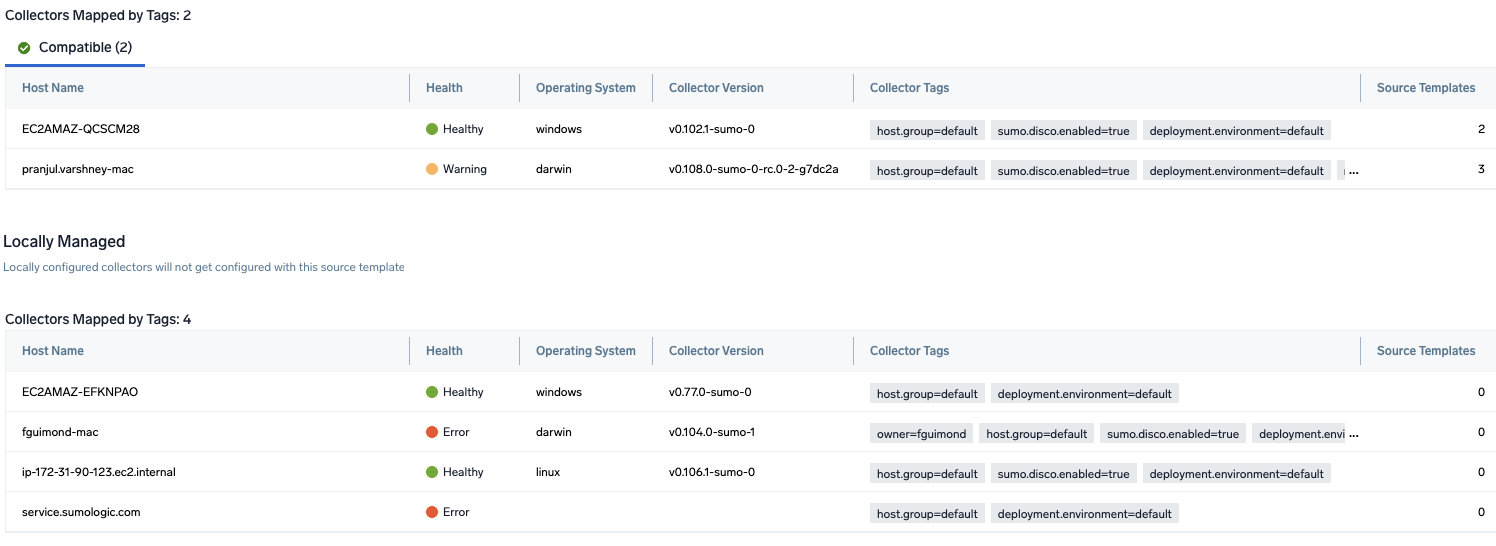
- Click Next to complete the source template creation. In the background, the system will apply the configuration to all the linked collectors and will start collecting the respective telemetry data from the remote host (in the example, it would start collecting Apache error logs).
- Click the Log Search or Metrics Search icons to search for and analyze your data collected for this source template.
Sample log messages
Here's a sample log message in a non-Kubernetes environment.
5275:S 17 Mar 2021 19:13:38.138 * MASTER <-> REPLICA sync: Finished with success
Sample queries
Logs
This sample query is from the Redis - Logs dashboard > Logs panel.
db.cluster.name=* sumo.datasource="redis"
| json auto maxdepth 1 nodrop
| if (isEmpty(log), _raw, log) as message
| count by message
| limit 100
| fields message
Metrics
This sample query is from the Redis - Cluster Operations dashboard Metrics panel.
(cmd=set* or cmd=get* or cmd=incr* or cmd=decr* or cmd=mget or cmd=mset* or cmd=strlen or cmd=psetex or cmd=append)
deployment.environment=* db.cluster.name=* db.node.name=*
| delta
| sum
Viewing Redis dashboards
Logs
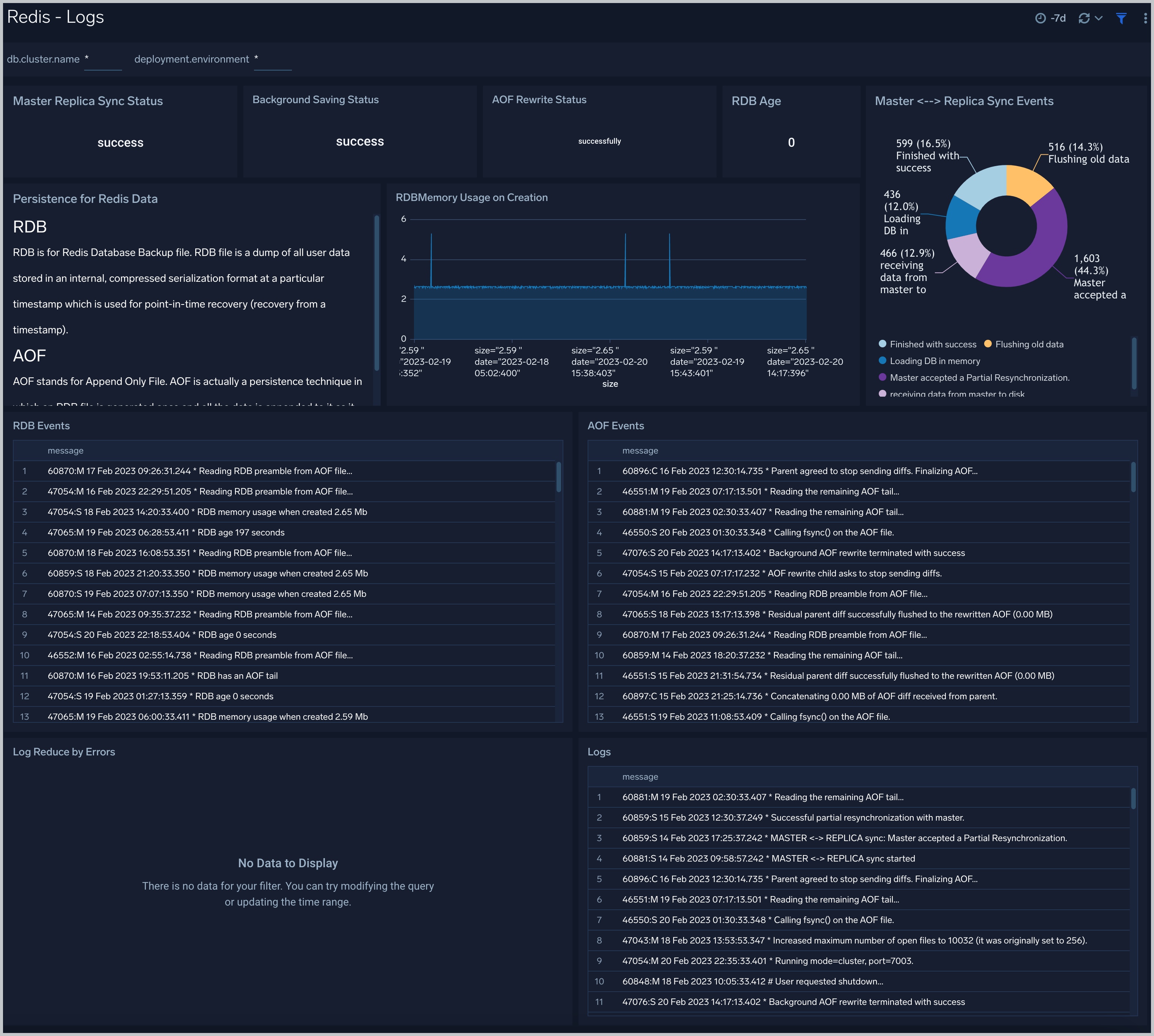
The Redis - Logs dashboard provides a detailed analysis based on logs. The panels provide details such as RDBMemory Usage, events, RDB, and AOF events.
Use this dashboard to:
- Review errors and warnings generated by the server.
- Review the RDBMemory Usage, events, RDB, and AOF events.
Overview
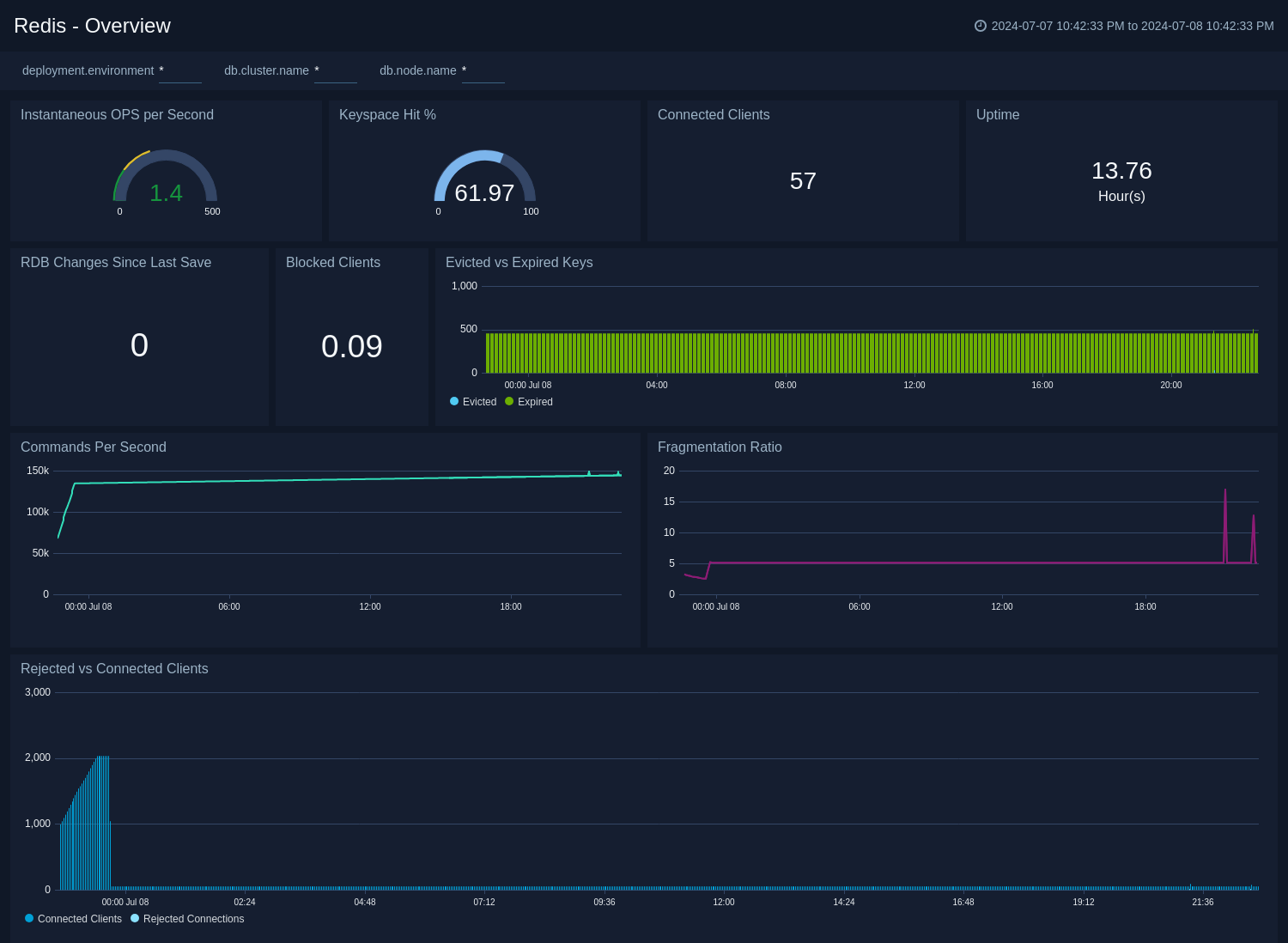
The Redis - Overview dashboard provides an at-a-glance view of the Redis server status and error logs, along with database metrics.
Use this dashboard to review keyspace hit, connected clients, Uptime, Evicted vs Expired Keys, and Commands Per Seconds.
Cluster Operations
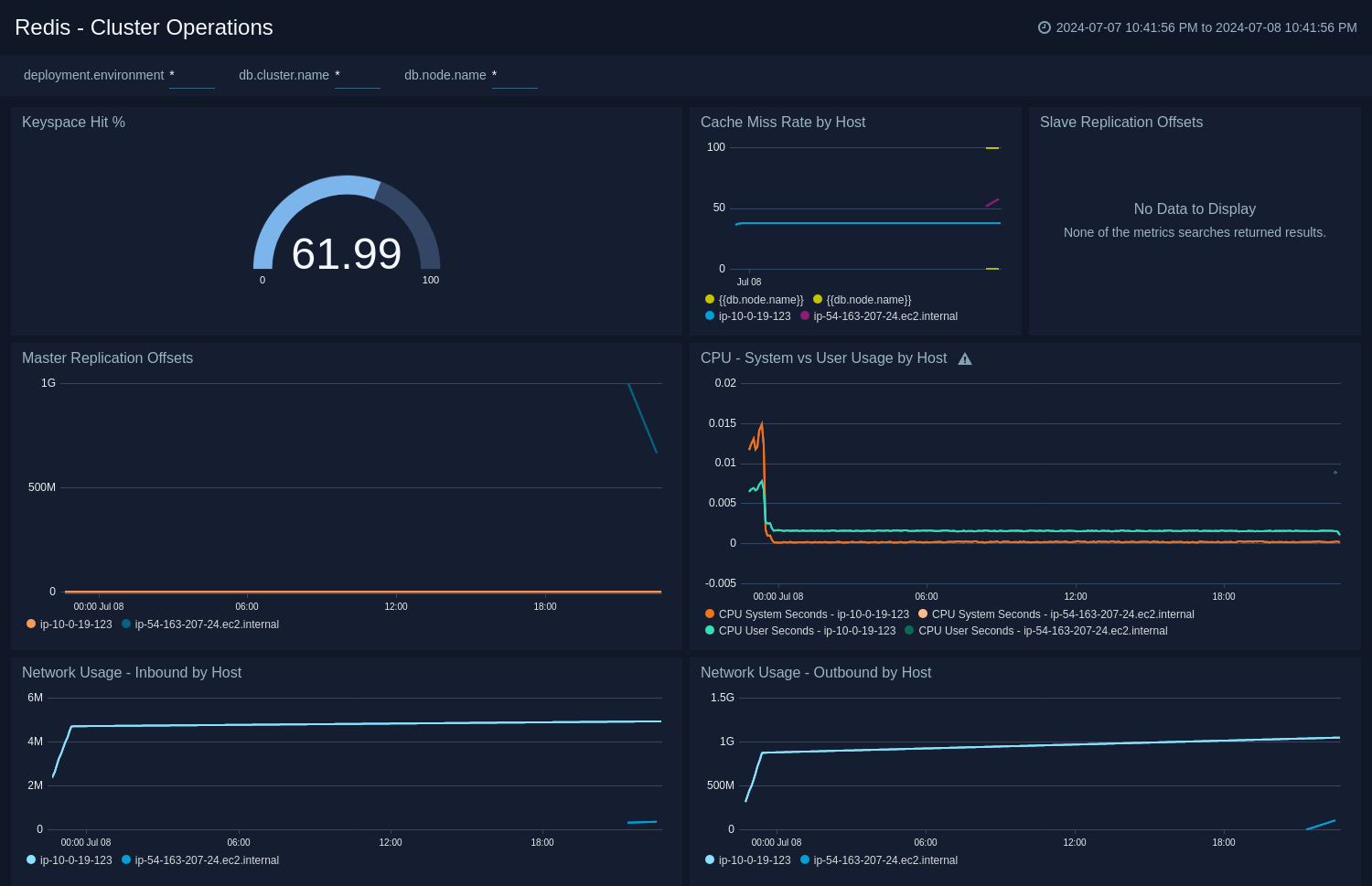
The Redis - Cluster Operations Operations dashboard provides a high-level view of the activity and health of Master and Slaves on your network. Dashboard panels display visual graphs and detailed information on cache rate and most importantly, resource usage.
Use this dashboard to review keyspace hit, Cache miss rate by host, CPU - System vs User usage by host, and Network Usage - Inbound/Outbound by Host.
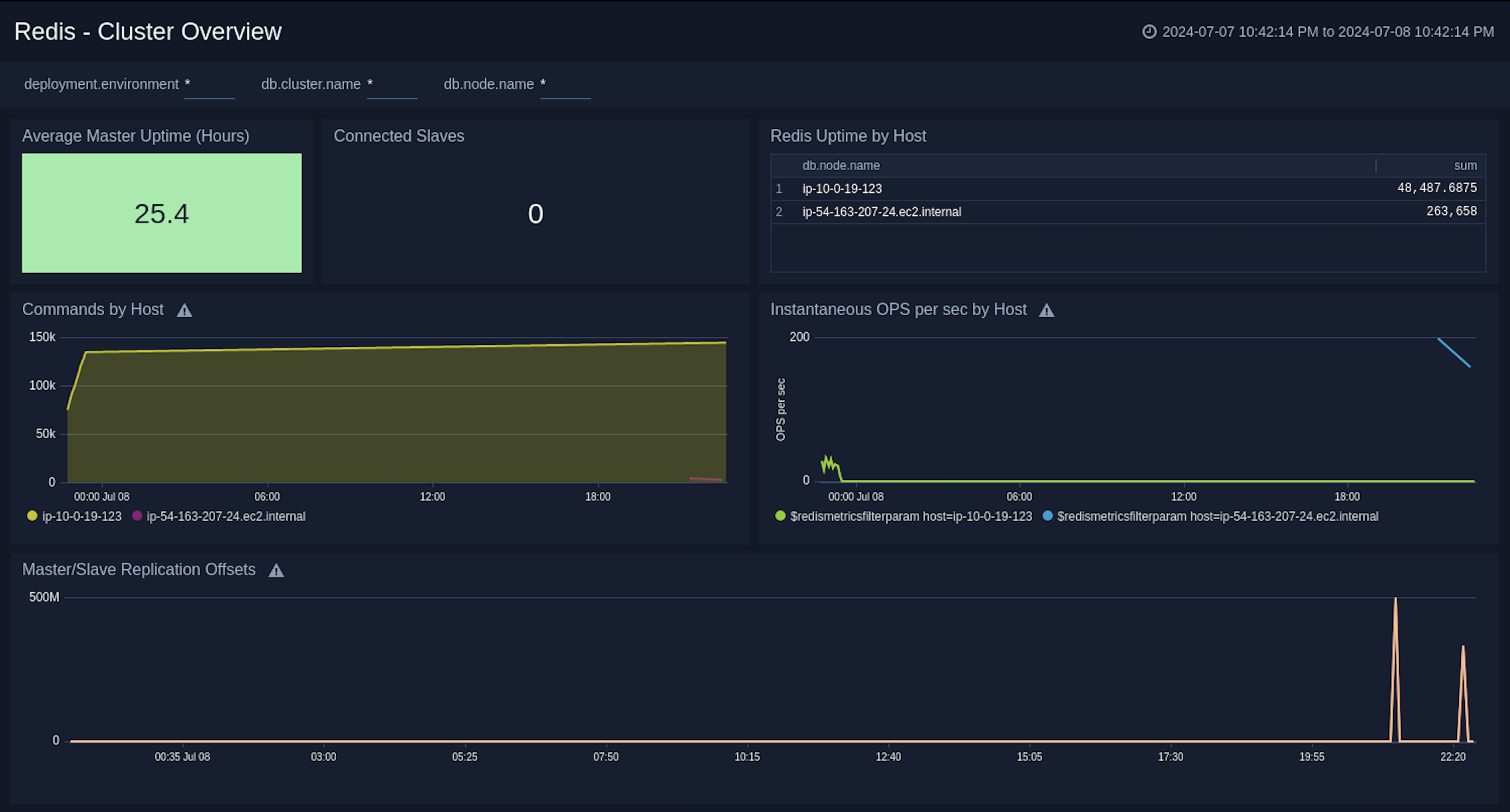
Cluster Overview
The Redis - Cluster Overview dashboard provides a high-level view of cluster infrastructure, comparisons, and trends.
Use this dashboard to review Average Master Uptime, Connected Slaves, Redis Uptime by Host, Commands by Host, and Instantaneous OPS per sec by Host.
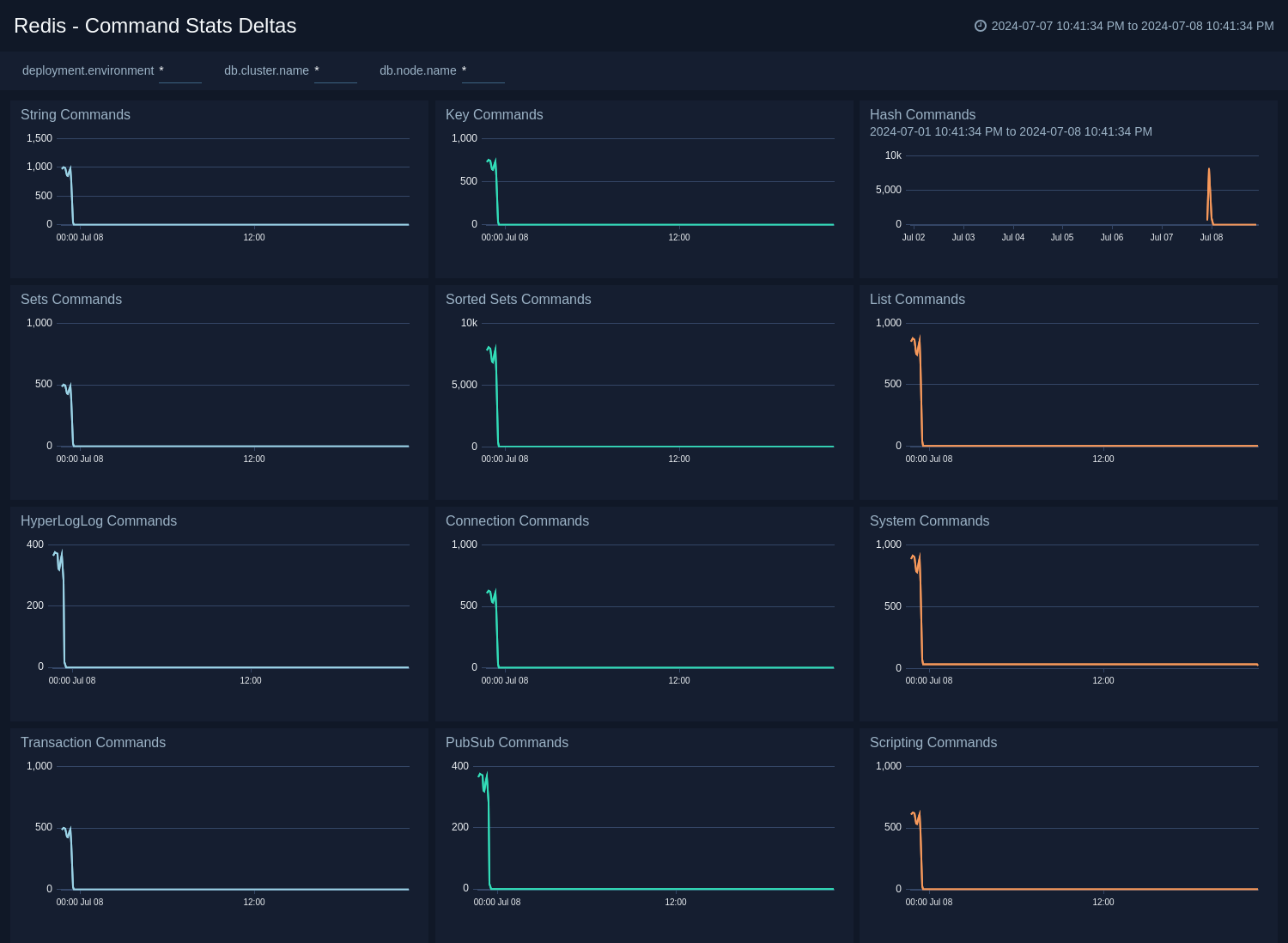
Command Stats Delta
The Redis - Command Stats Delta dashboard provides an at-a-glance view of commands running on your Redis server.
Use this dashboard to review String Commands, Key Commands, Hash Commands, Sets Commands, Sorted Sets Commands, List Commands, Transaction Commands, and Scripting Commands.
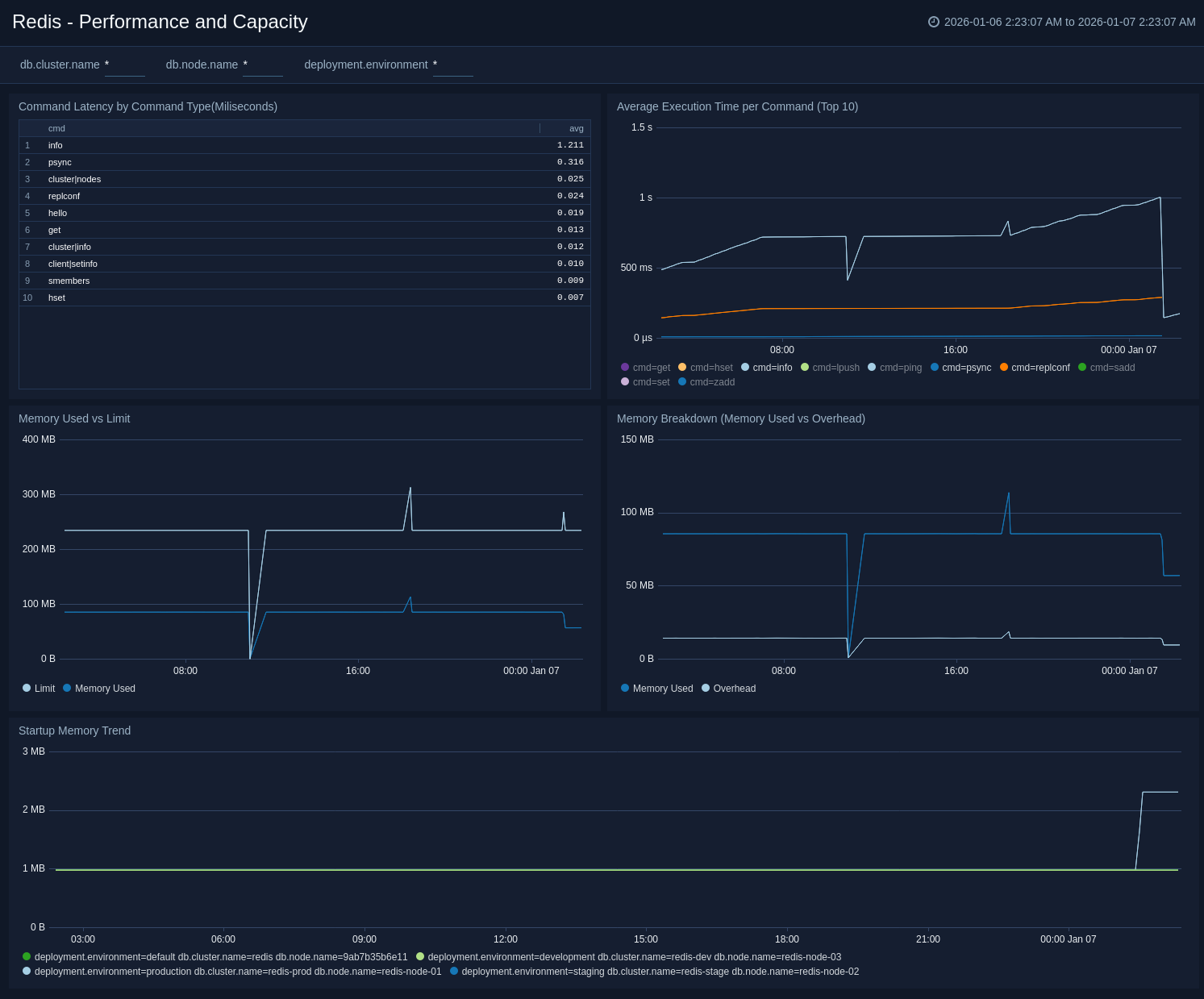
Performance and Capacity
The Redis – Performance and Capacity dashboard provides at-a-glance view of key Redis performance metrics and resource limits. This dashboard offers detailed insights into command latency analysis, execution time tracking, memory consumption patterns, and capacity limits, enabling teams to monitor performance, optimize resource usage, and proactively prevent capacity-related issues.
Create monitors for Redis app
From your App Catalog:
- From the Sumo Logic navigation, select App Catalog.
- In the Search Apps field, search for and then select your app.
- Make sure the app is installed.
- Navigate to What's Included tab and scroll down to the Monitors section.
- Click Create next to the pre-configured monitors. In the create monitors window, adjust the trigger conditions and notifications settings based on your requirements.
- Scroll down to Monitor Details.
- Under Location click on New Folder.
note
By default, monitor will be saved in the root folder. So to make the maintenance easier, create a new folder in the location of your choice.
- Enter Folder Name. Folder Description is optional.
tip
Using app version in the folder name will be helpful to determine the versioning for future updates.
- Click Create. Once the folder is created, click on Save.
Redis alerts
| Name | Description | Alert Condition | Recover Condition |
|---|---|---|---|
Redis - High Memory Fragmentation Ratio | This alert is triggered when the ratio of Redis memory usage to Linux virtual memory pages (mapped to physical memory chunks) is higher than 1.5. A high ratio will lead to swapping and can adversely affect performance. | Count > 1.5 | Count < = 1.5 |
Redis - Instance Down | This alert is triggered if the Redis instance is down for 5 minutes. | Missing Data | Data Found |
Redis - Rejected Connections | This alert is triggered when some connections to a Redis cluster have been rejected. | Count > 0 | Count < = 0 |
Redis - Replication Broken | This alert is triggered when a Redis instance has lost all slaves. This will affect the redundancy of data stored in Redis. We suggest you to review how replication has been configured. | Count < 1 | Count > = 1 |
Redis - Replication Offset | This alert is triggered when the replication offset in a given Redis cluster is greater than 1 MB for last 5 minutes. We suggest you to review how replication has been configured. | Count > = 1 | Count < 1 |
Redis - Too Many Connections | This alert is triggered when a given Redis server has too many connections (default is 100). | Count > 100 | Count < = 100 |