Secure your AWS infrastructure with a single click
Cloud infrastructure security for AWS provides enhanced insight into threat activity via a unified security and compliance audit view of your AWS infrastructure. Leveraging AWS-native tools and telemetry, it accelerates development, operations, security, and reliability management teams in maintaining security visibility into their environment, managing their risk and attack surface.
Infrastructure overview dashboard
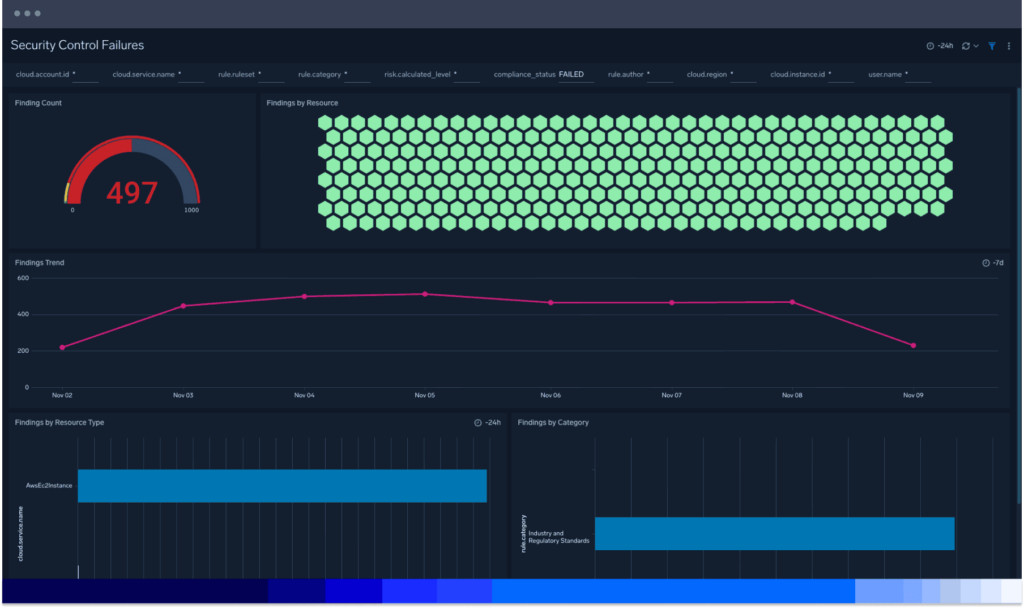
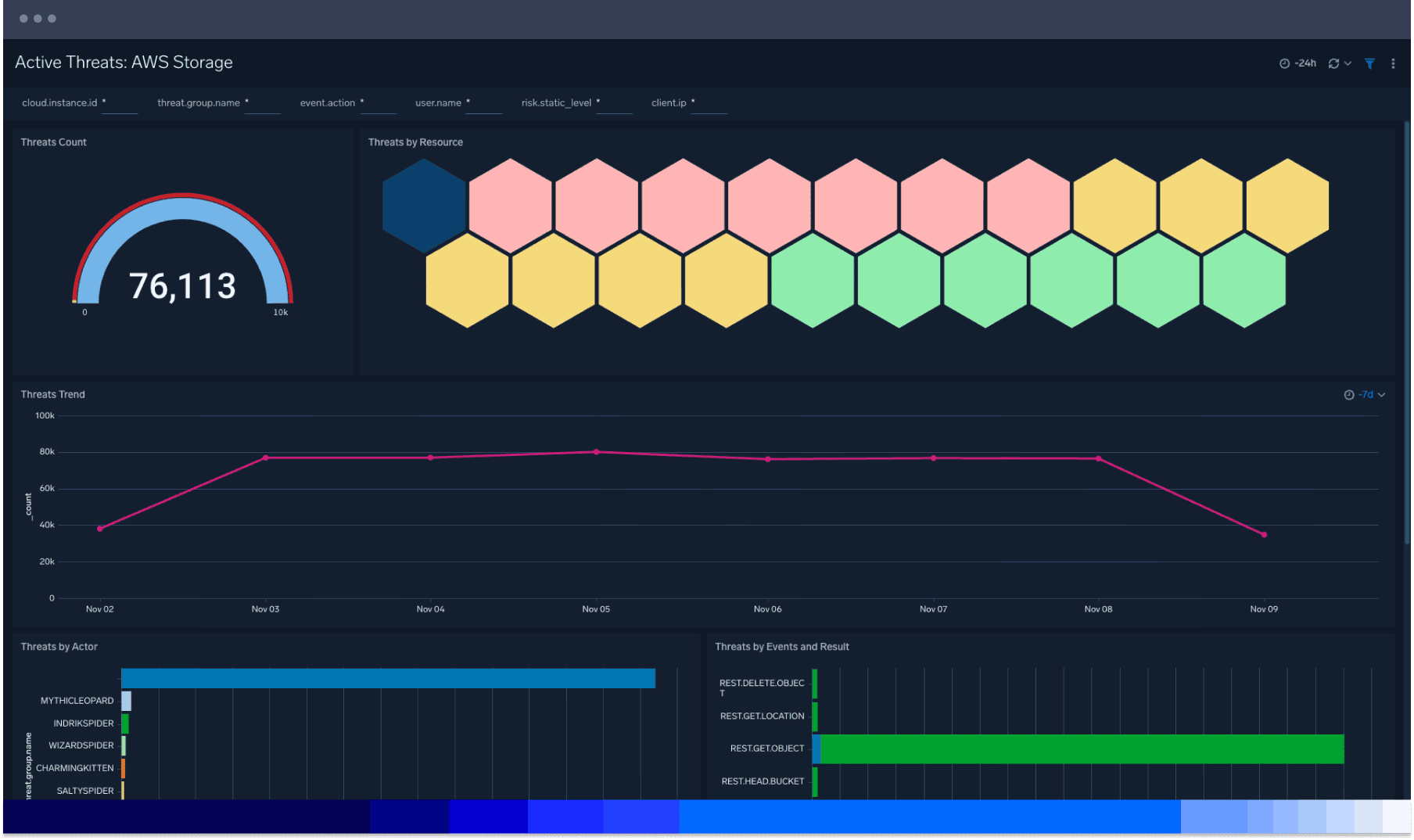
Quickly review and identify security incidents and threats at a glance with the overview dashboard. Ingest telemetry from essential AWS services for enhanced visibility into your AWS environment with visualizations of critical areas of your cloud infrastructure security posture. Rapidly audit the overall state of security readiness.
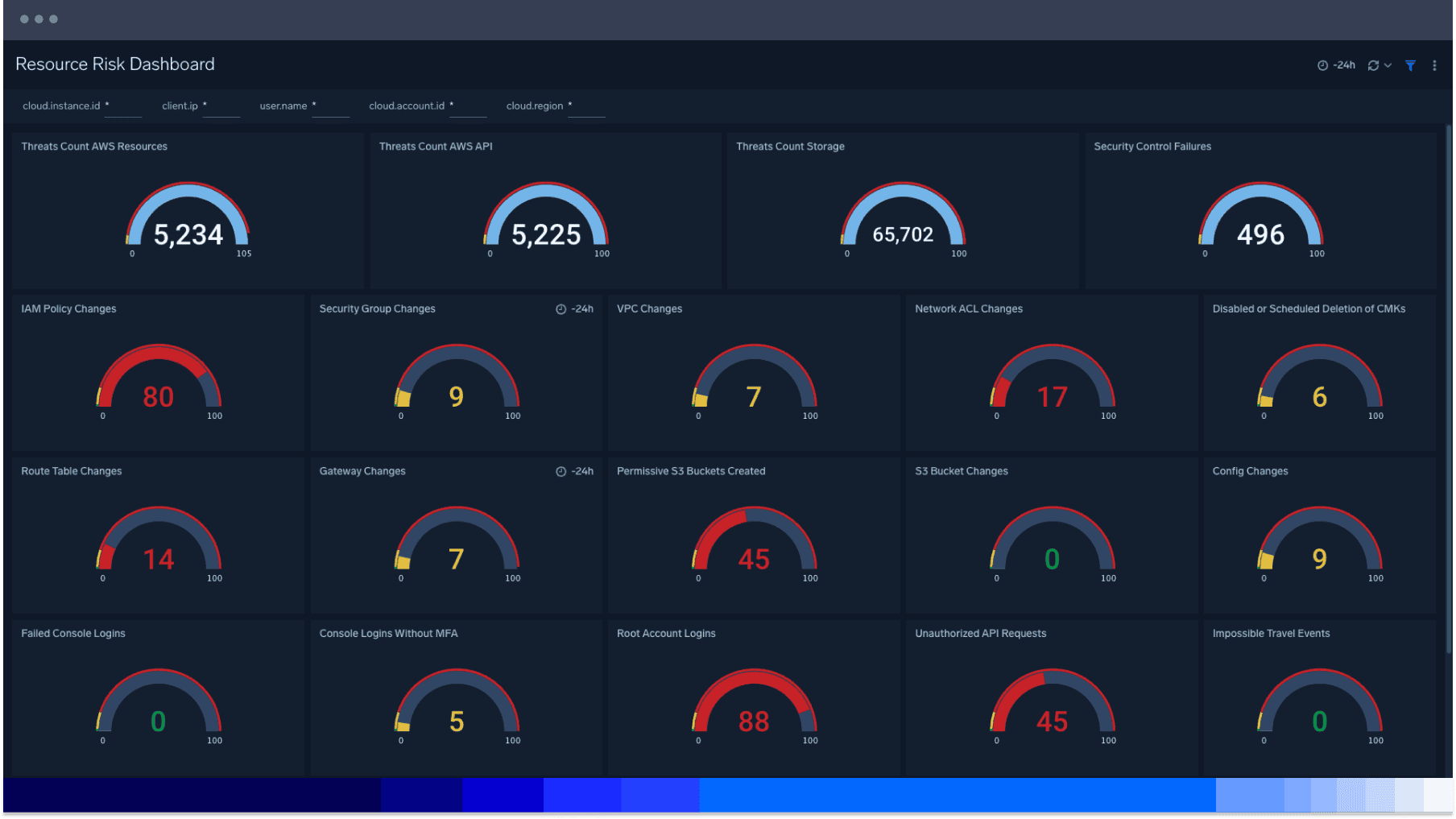
Steady pulse of your risk profile
Manage your evolving threat landscape
Control access activities
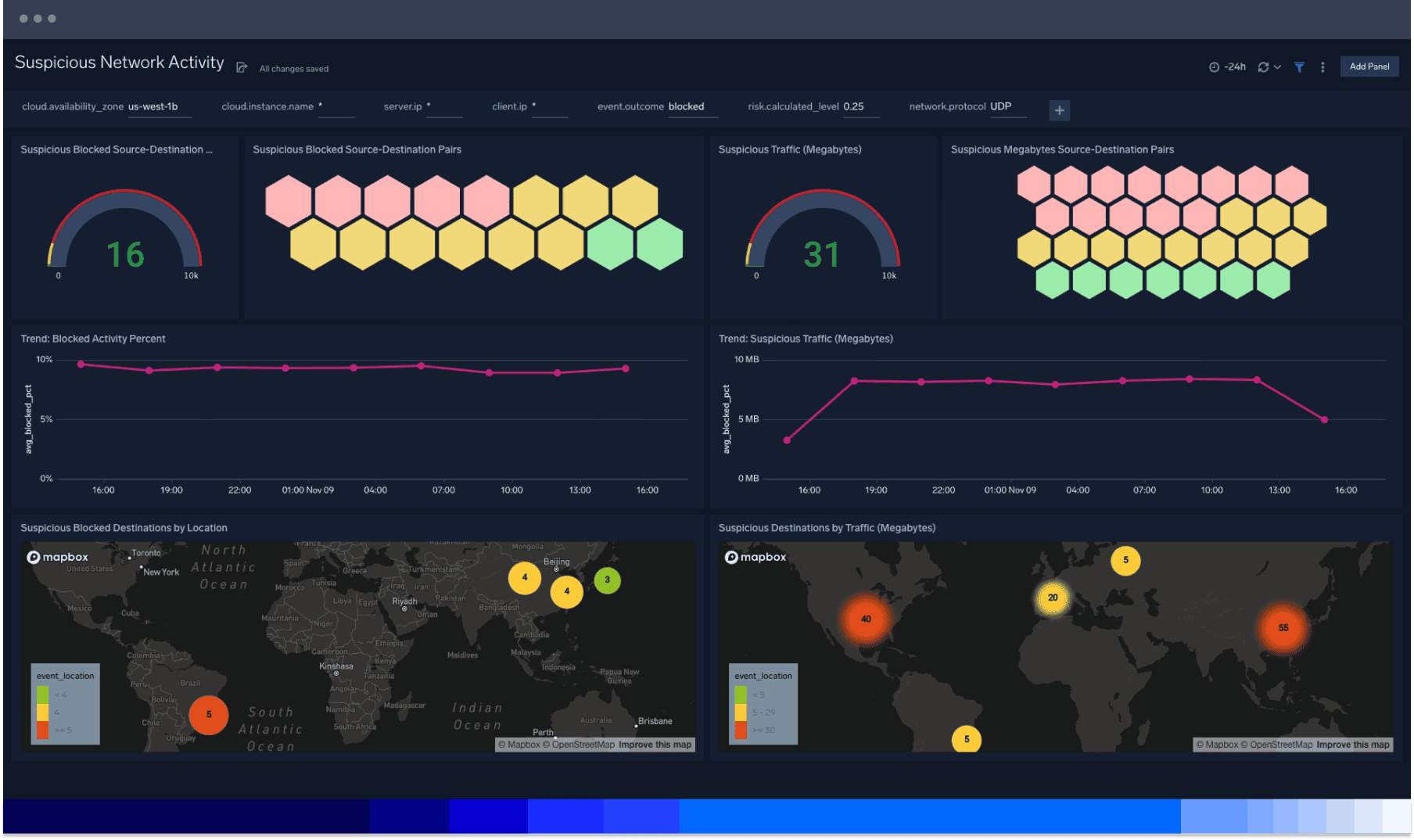
Know your cloud attack surface
Cut through the noise of complex cloud environments to manage your attack surface with Sumo Logic’s cloud-scale collection, storage and security analytics. Easily pinpoint vulnerabilities created by aging or drifting configuration, access rights, or software with cloud infrastructure security for AWS.
Combat complexity
Distill insights from across your entire microservices architecture and enable teams to collaborate and resolve the hardest questions facing digital companies.
Increase visibility
Accelerate security and reliability management workflows across development and operations, maintaining security visibility, and managing your risk and cloud attack surface.
Maximize efficiency
Enable practitioners of all skill levels to manage their cloud attack surface easily with curated, out-of-the-box security content. Security personnel can share dashboards and jointly resolve security issues as they arise from anywhere.
Optimize costs
With Flex Licensing, you get unlimited ingest and unlimited users. Store all your data for compliance, consistent with an extensive list of regulatory frameworks, without the need for cold storage or data rehydration.
Additional resources

IDC’s ROI report: The business value of Sumo Logic

Micro Lesson: cloud infrastructure security for AWS

Security best practices
Monitor and secure 10,000 clouds

Data is at the heart of cloud-native bank

Faster incident detection and response with Cloud SIEM
FAQ
Still have questions?
Cloud infrastructure security is a set of practices designed to protect cloud environments, sensitive data, and supporting systems from unauthorized access and security threats. This includes measures for cloud data security, identity and access management (IAM), application security, network security, and the protection of cloud resources and services.
Cloud infrastructure consists of the hardware and software needed to support cloud services for customers. It includes three main models:
- Private cloud: Exclusively used by a single organization. Private cloud infrastructure may be managed by on-site IT staff or an external provider and requires organizations to invest in their own hardware.
- Public cloud: Operated by third-party providers, such as Google Cloud, AWS, and Microsoft Azure, and uses a multi-tenant model. Customers pay on a per-use basis for storage and computing power.
- Hybrid cloud: Combines private and public cloud environments, allowing sensitive data to be stored on private servers while less critical applications run in the public cloud.
Identity and Access Management (IAM):
- Use multi-factor authentication (MFA) and role-based access controls (RBAC).
- Regularly review permissions based on the principle of least privilege.
Data encryption:
- Encrypt data both in transit and at rest, using tools like AWS KMS or Azure Key Vault for key management.
Network security:
- Use virtual private clouds (VPCs) and security groups to control traffic.
- Monitor network traffic for suspicious activities.
Monitoring and logging:
- Enable comprehensive logging and use tools like security information and event management (SIEM) solutions for monitoring.
- Set up alerts for potential security incidents.
Incident response and recovery:
- Develop and test an incident response plan.
- Regularly back up critical data and test restoration processes.
Patch management:
- Regularly update software and implement automated patching.
- Conduct vulnerability assessments and penetration testing.
Compliance and governance:
- Adhere to industry-specific compliance requirements and conduct regular audits.
API security:
- Secure APIs with authentication, use API gateways, and implement Web Application Firewalls (WAFs).
Container security (if applicable):
- Use container security practices, such as scanning images and using secure orchestration tools like Kubernetes.
